HP Vectra XU 6/XXX HP Vectra XU6/150 PC - User’s Guide - Page 33
Further Suggestions, Summary Recommendations
 |
View all HP Vectra XU 6/XXX manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 33 highlights
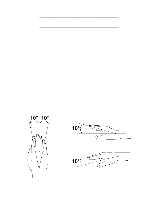
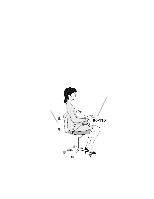
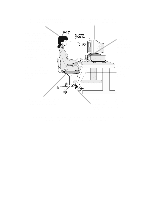
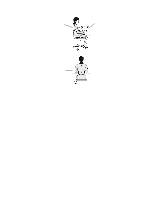
Incoming light should be shielded or diffused to prevent glare and distracting reflection. In cases where strong sunlight is a problem, curtains, adjustable shades, or display hoods are recommended. If possible, try not to position the display in front of windows where glare, high contrast, and reflections will interfere with your screen presentations. Try to position the display so the screen is at a right angle to the window. FURTHER SUGGESTIONS • Have your eyes checked on a regular basis and ensure your eyeglass prescription is suitable for working on a display screen. • Look away from the screen from time to time to help reduce eye strain. Focus on distant objects briefly. Also, blinking periodically helps lubricate the eyes. • Avoid holding your muscles tensed for long periods of time. Keep your fingers and body relaxed. • Changing tasks frequently will help prevent muscle stiffness. For example: alternating between using the keyboard, writing, filing, and moving around in your work environment, helps keep muscles loose. • When prolonged screen work is required, take frequent short breaks. As a rule of thumb, a five or ten minute break every hour is a good idea. Short frequent breaks are more beneficial than longer less frequent breaks. Data shows that people who work for long lengths of time without a break are more prone to injury. • Occasionally stretch the muscles in your hands, arms, shoulders, neck and back. You should stretch at least as often as you take your breaks, that is, at least once per hour. • Discomfort, if any, may be alleviated by use of alternative ergonomic designs and accessories such as: ergonomic personalized chairs, wrist rests, keyboard trays, alternative input devices, non-prescription eye glasses, glare screens, and more. Seek additional information from the sources available to you, including your employer, doctor, local office supply store, and the bibliography provided at the end of this section. • If you experience any discomfort, discontinue use and see a doctor as soon as possible. If you want additional information on VDT setup, ergonomics and related topics, consult your employer and the sources listed at the end of this section. SUMMARY RECOMMENDATIONS The recommendations in the following illustrations are drawn from the latest available international ergonomic standards and recommendations, including ISO 9241 and ANSI/HFS 100-1988.