HP GbE2c HP GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch for c-Class BladeSystem Application Gu - Page 129
Remote monitoring, Introduction, Overview, RMON group 1—statistics
 |
UPC - 808736802215
View all HP GbE2c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 129 highlights
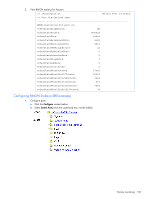
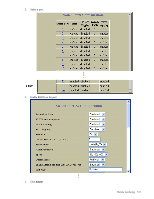
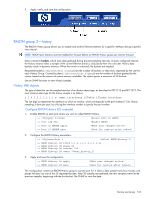
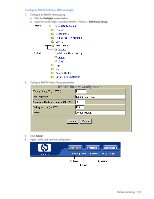
Remote monitoring Introduction Remote Monitoring (RMON) allows network devices to exchange network monitoring data. RMON performs the following major functions: • Gathers cumulative statistics for Ethernet interfaces • Tracks a history of statistics for Ethernet interfaces • Creates and triggers alarms for user-defined events Overview The RMON MIB provides an interface between the RMON agent on the switch and an RMON management application. The RMON MIB is described in RFC 1757. The RMON standard defines objects that are suitable for the management of Ethernet networks. The RMON agent continuously collects statistics and proactively monitors switch performance. RMON allows you to monitor traffic flowing through the switch. The switch supports the following RMON Groups, as described in RFC 1757: • Group 1: Statistics • Group 2: History • Group 3: Alarms • Group 9: Events RMON group 1-statistics The switch supports collection of Ethernet statistics as outlined in the RMON statistics MIB, in reference to etherStatsTable. You can enable RMON statistics on a per-port basis, and you can view them using the following command: /stat/port x/rmon. RMON statistics are sampled every second, and new data overwrites any old data on a given port. NOTE: RMON port statistics must be enabled for the port before you can view RMON statistics. Configuring RMON Statistics (CLI example) 1. Enable RMON on each port where you wish to collect RMON statistics. >> /cfg/port 23/rmon (Select Port 23 RMON) >> Port 23 RMON# ena (Enable RMON) >> Port 23 RMON# apply (Make your changes active) >> Port 23 RMON# save (Save for restore after reboot) Remote monitoring 129