HP GbE2c HP GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch for c-Class BladeSystem Application Gu - Page 70
Quality of Service, Introduction, Overview - basic system configuration
 |
UPC - 808736802215
View all HP GbE2c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 70 highlights
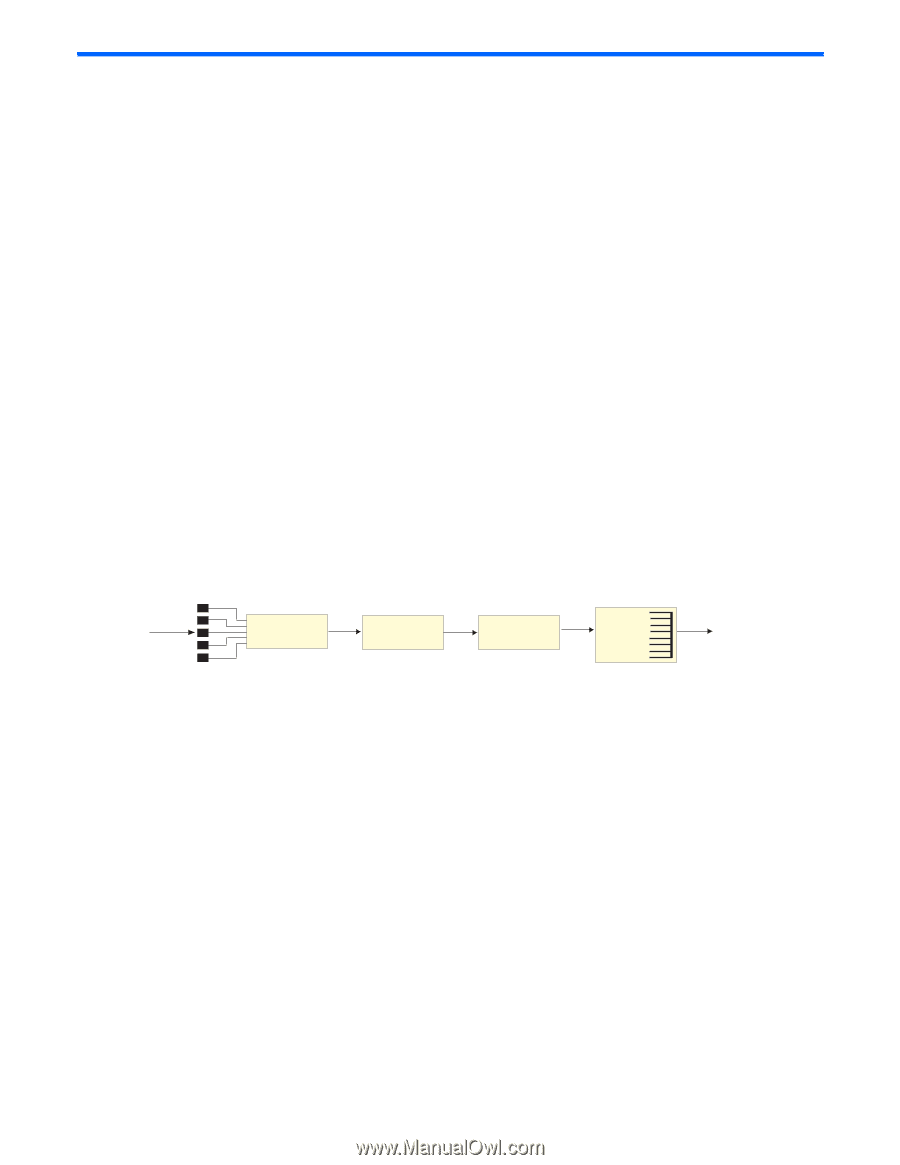
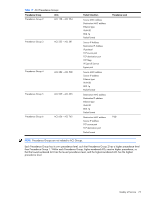
Quality of Service Introduction Quality of Service features allow you to allocate network resources to mission-critical applications at the expense of applications that are less sensitive to such factors as time delays or network congestion. You can configure your network to prioritize specific types of traffic, ensuring that each type receives the appropriate Quality of Service (QoS) level. The following topics are discussed in this section: • Quality of Service Overview • Using ACL Filters • Using DSCP Values to Provide QoS • Using 802.1p Priorities to Provide QoS • Queuing and Scheduling Overview QoS helps you allocate guaranteed bandwidth to the critical applications, and limit bandwidth for less critical applications. Applications such as video and voice must have a certain amount of bandwidth to work correctly; using QoS, you can provide that bandwidth when necessary. Traffic for applications that are sensitive to timing out or cannot tolerate delay can be assigned to a high-priority queue. By assigning QoS levels to traffic flows on your network, you can ensure that network resources are allocated where they are needed most. QoS features allow you to prioritize network traffic, thereby providing better service for selected applications. The following figure shows the basic QoS model used by the GbE2c. Figure 11 QoS model Ingress Ports Classify Packets Meter Traffic Perform Actions Queue and Egress Schedule ACL Filter ACL Meter Drop/Pass/ Re-Mark COS Queue The GbE2c uses the Differentiated Services (DiffServ) architecture to provide QoS functions. DiffServ is described in IETF RFCs 2474 and 2475. With DiffServ, you can establish policies to direct traffic. A policy is a traffic-controlling mechanism that monitors the characteristics of the traffic, (for example, its source, destination, and protocol) and performs a controlling action on the traffic when certain characteristics are matched. The GbE2c can classify traffic by reading the IEEE 802.1p priority value, or by using filters to match specific criteria. When network traffic attributes match those specified in a traffic pattern, the policy instructs the GbE2c to perform specified actions on each packet that passes through it. The packets are assigned to different Class of Service (COS) queues and scheduled for transmission. The basic GbE2c QoS model works as follows: • Classify traffic: • Read 802.1p Priority • Match ACL filter parameters • Meter traffic: • Define bandwidth and burst parameters • Select actions to perform on in-profile and out-of-profile traffic • Perform actions: • Drop packets • Pass packets • Mark DSCP or 802.1p Priority • Set COS queue (with or without re-marking) Quality of Service 70