HP GbE2c HP GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch for c-Class BladeSystem Application Gu - Page 22
How TACACS+ authentication works, TACACS+ authentication features, Authorization, Table 4 - manual
 |
UPC - 808736802215
View all HP GbE2c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 22 highlights
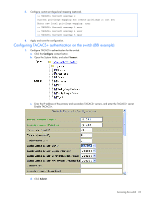
• TACACS+ offers full packet encryption whereas RADIUS offers password-only encryption in authentication requests. • TACACS+ separates authentication, authorization, and accounting. How TACACS+ authentication works TACACS+ works much in the same way as RADIUS authentication. 1. Remote administrator connects to the switch and provides user name and password. NOTE: The user name and password can have a maximum length of 128 characters. The password cannot be left blank. 2. Using Authentication/Authorization protocol, the switch sends request to authentication server. 3. Authentication server checks the request against the user ID database. 4. Using TACACS+ protocol, the authentication server instructs the switch to grant or deny administrative access. During a session, if additional authorization checking is needed, the switch checks with a TACACS+ server to determine if the user is granted permission to use a particular command. TACACS+ authentication features Authentication is the action of determining the identity of a user, and is generally done when the user first attempts to log in to a device or gain access to its services. Switch software supports ASCII inbound login to the device. PAP, CHAP and ARAP login methods, TACACS+ change password requests, and one-time password authentication are not supported. Authorization Authorization is the action of determining a user's privileges on the device, and usually takes place after authentication. The default mapping between TACACS+ authorization privilege levels and switch management access levels is shown in the table below. The privilege levels listed in the following table must be defined on the TACACS+ server. Table 4 Default TACACS+ privilege levels User access level TACACS+ level user 0 oper 3 admin 6 Alternate mapping between TACACS+ privilege levels and GbE2c management access levels is shown in the table below. Use the command /cfg/sys/tacacs/cmap ena to use the alternate TACACS+ privilege levels. Table 5 Alternate TACACS+ privilege levels User access level TACACS+ level user oper admin 0-1 6- 8 14-15 You can customize the mapping between TACACS+ privilege levels and GbE2c management access levels. Use the command /cfg/sys/tacacs/usermap to manually map each TACACS+ privilege level (0-15) to a corresponding GbE2c management access level (user, oper, admin, none). If the remote user is authenticated by the authentication server, the GbE2c verifies the privileges of the remote user and authorizes the appropriate access. When both the primary and secondary authentication servers are not reachable, the administrator has an option to allow backdoor access via the console only or console and Telnet access. The default value is disable for Telnet access and enable for console access. The administrator also can enable secure backdoor (/cfg/sys/tacacs/secbd) to allow access if both the primary and secondary TACACS+ servers fail to respond. Accessing the switch 22