HP GbE2c HP GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch for c-Class BladeSystem Application Gu - Page 164
ICMP;IGMP;TCP;UDP: filtering criteria, Open Shortest Path First OSPF - trunk cisco
 |
UPC - 808736802215
View all HP GbE2c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
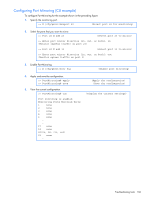
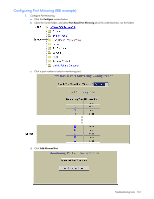
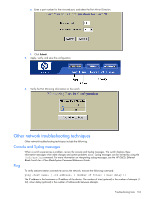
Page 164 highlights
Index 8 802.1x port states, 41 A accessing the switch: defining source IP addresses, 17; RADIUS authentication, 18; security, 17; using the command line interface (CLI), 10 ACL Blocks and Groups, 74 ACL configuration examples, 75 ACL filters, 71 active-active redundancy, 147 allowable source IP addresses, 17 B BBI: See Browser-Based Interface, 110 Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BPDU), 55 broadcast domains, 43, 47 Browser-Based Interface, 110 C Cisco EtherChannel, 31 Class of Service queueCOS queue, 86 Command Line Interface, 110 command line interface (CLI), 10 configuration, 31 configuration rules: port mirroring, 31; trunking, 31; VLANs, 31 configuring: OSPF, 116 configuring SNMP trap hosts, 15 console messages, 162 customer support tools, 163 D default gateway: configuration example, 11, 90 Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP)DSCP, 80 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, 92 E EAPoL configuration guidelines, 42 EtherChannel, as used with port trunking, 31 Extensible Authentication Protocol over LAN (EAPoL)EAPoL, 39 F switch failover: overview, 146 Fast Uplink Convergence, 61 fault tolerance, port trunking, 31 FDB static entries, 54 frame tagging, 44 G default gateway, 89 H high-availability, 8, 140 I IBM DirectorSNMP: IBM Director, 12 IEEE 802.1Q VLAN tagging, 44, 47 IEEE standards: 802.1x, 39 IGMP Filtering, configuring (BBI example), 102 IGMP Filtering, configuring (CLI example), 99 IGMP Snooping, 97 IGMP Snooping, configuring (BBI example), 100 IGMP Snooping, configuring (CLI example), 98 IP address: routing example, 89 IP interfaces: configuring, 11; example configuration, IP interface configuration, 92; VLAN #1 (default), 47; VLANs, 47 IP routing, 87; default gateway configuration, 11, 90; IP interface configuration, 90, 92; IP interfaces example configuration, 90 IP subnets: routing; IP subnets, 88; routing, 89 IP subnets, VLANs, 43 J fragmenting jumbo frames: fragmenting to normal size; routing, 87 L LACP, 37 Link Aggregation Control Protocol, 37 logical segment, 43 LSAs, 109 M Main Menu, command line interface (CLI), 10 media access control (MAC) address, 11 meter, 74 mirroring ports, 159 monitoring ports, 159 MSTP, 62 multi-links between switches, using port trunking, 30 multiple spanning tree groups, 57 N network management, 12 O Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), 107 ICMP;IGMP;TCP;UDP: filtering criteria, 71 OSPF: overview, 107 OSPF: area types, 107 OSPF: neighbors, 109 OSPF: link state database, 109 OSPF: route summarization, 112 OSPF: default route; OSPF, 112 OSPF: virtual link, 113 OSPF: authentication, 114 OSPF: host routes; OSPF, 115 OSPF: external routes, 116 OSPF configuration examples, 116, 117, 124, 126, 127 OSPF configuration, verifying, 128 P ping, 162 Port Fast Forwarding, 60 port mirroring: configuration rules, 31; troubleshooting, 159 port trunking, 31 port trunking, fault tolerance, 31 Port-based Network Access control, 39 Port-based traffic control, 42 ports: monitoring, 159; physical, 44 priority value (802.1p), 81 PVID (port VLAN ID), 43 Q Quality of Service, 70 queuing and scheduling, 86 R RADIUS: port 1812 and 1645, 71; port 1813, 71 redundancy: active-active, 147; VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol), 147 re-mark, 75 Index 164