HP GbE2c HP GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch for c-Class BladeSystem Application Gu - Page 93
DHCP relay agent configuration, In GbE2c implementation - vlan redundancy
 |
UPC - 808736802215
View all HP GbE2c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 93 highlights
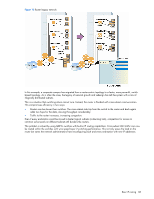
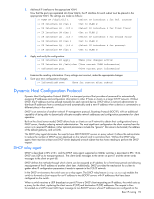
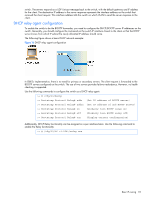
switch. The servers respond as a UDP Unicast message back to the switch, with the default gateway and IP address for the client. The destination IP address in the server response represents the interface address on the switch that received the client request. This interface address tells the switch on which VLAN to send the server response to the client. DHCP relay agent configuration To enable the switch to be the BOOTP forwarder, you need to configure the DHCP/BOOTP server IP addresses on the switch. Generally, you should configure the command on the switch IP interface closest to the client so that the DHCP server knows from which IP subnet the newly allocated IP address should come. The following figure shows a basic DHCP network example: Figure 16 DHCP relay agent configuration In GbE2c implementation, there is no need for primary or secondary servers. The client request is forwarded to the BOOTP servers configured on the switch. The use of two servers provides failover redundancy. However, no health checking is supported. Use the following commands to configure the switch as a DHCP relay agent: >> # /cfg/l3/bootp >> Bootstrap Protocol Relay# addr (Set IP address of BOOTP server) >> Bootstrap Protocol Relay# addr2 (Set IP address of 2nd BOOTP server) >> Bootstrap Protocol Relay# on (Globally turn BOOTP relay on) >> Bootstrap Protocol Relay# off (Globally turn BOOTP relay off) >> Bootstrap Protocol Relay# cur (Display current configuration) Additionally, DHCP Relay functionality can be assigned on a per interface basis. Use the following command to enable the Relay functionality: >> # /cfg/l3/if /relay ena Basic IP routing 93