HP GbE2c HP GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch for c-Class BladeSystem Application Gu - Page 98
IGMP Filtering, Configuring the range, Static multicast router, IGMP Snooping configuration example
 |
UPC - 808736802215
View all HP GbE2c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 98 highlights
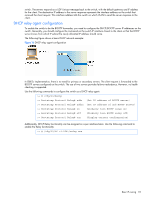
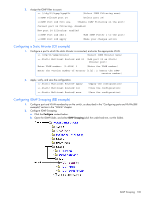
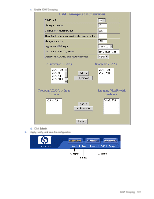
IGMP Filtering With IGMP Filtering, you can allow or deny a port to send and receive multicast traffic to certain multicast groups. Unauthorized users are restricted from streaming multicast traffic across the network. If access to a multicast group is denied, IGMP Membership Reports from the port for that group are dropped, and the port is not allowed to receive IP multicast traffic from that group. If access to the multicast group is allowed, Membership Reports from the port are forwarded for normal processing. To configure IGMP Filtering, you must globally enable IGMP Filtering, define an IGMP Filter, assign the filter to a port, and enable IGMP Filtering on the port. To define an IGMP Filter, you must configure a range of IP multicast groups, choose whether the filter will allow or deny multicast traffic for groups within the range, and enable the filter. NOTE: Low-numbered filters take precedence over high-number filters. For example, the action defined for IGMP Filter 1 supersedes the action defined for IGMP Filter 2. Configuring the range Each IGMP Filter allows you to set a start and end point that defines the range of IP addresses upon which the filter takes action. Each IP address in the range must be between 224.0.0.0 and 239.255.255.255. Configuring the action Each IGMP Filter can allow or deny IP multicasts to the range of IP addresses configured. If you configure the filter to deny IP multicasts, then IGMP Membership Reports from multicast groups within the range are dropped. You can configure a secondary filter to allow IP multicasts to a small range of addresses within a larger range that a primary filter is configured to deny. The two filters work together to allow IP multicasts to a small subset of addresses within the larger range of addresses. The secondary filter must have a lower number than the primary filter, so that it takes precedence. Static multicast router A static multicast router (Mrouter) can be configured for a particular port on a particular VLAN. A static Mrouter does not have to be learned through IGMP Snooping. A total of eight static Mrouters can be configured on the switch. Only uplink (20-24) and interconnect ports (17-18) can accept a static Mrouter. A port that belongs to a trunk group cannot accept a static Mrouter, only Mrouters learned through IGMP Snooping. When you configure a static Mrouter on a VLAN, it replaces any dynamic Mrouters learned through IGMP Snooping. IGMP Snooping configuration example This section provides steps to configure IGMP Snooping on the switch, using the Command Line Interface (CLI) or the Browser-based Interface (BBI). Configuring IGMP Snooping (CLI example) 1. Configure port and VLAN membership on the switch, as described in the "Configuring ports and VLANs (CLI example)" section in the "VLANs" chapter. 2. Add VLANs to IGMP Snooping and enable the feature. >> /cfg/l3/igmp/snoop (Select IGMP Snooping menu) >> IGMP Snoop# ena (Enable IGMP Snooping) >> IGMP Snoop# apply (Make your changes active) IGMP Snooping 98