HP GbE2c HP GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch for c-Class BladeSystem Application Gu - Page 61
Configuring Port Fast Forwarding, Fast Uplink Convergence, Configuration guidelines - spanning tree
 |
UPC - 808736802215
View all HP GbE2c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 61 highlights
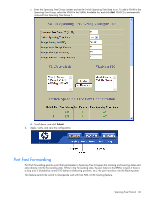
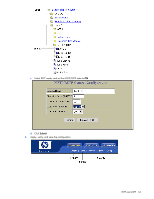
Configuring Port Fast Forwarding Use the following CLI commands to enable Port Fast Forwarding on an external port. >> # /cfg/l2/stp 1/port 20 (Select port 20) >> Spanning Tree Port 20# fastfwd ena (Enable Port Fast Forwarding) >> Spanning Tree Port 20# apply (Make your changes active) >> Spanning Tree Port 20# save (Save for restore after reboot) Fast Uplink Convergence Fast Uplink Convergence enables the switch to quickly recover from the failure of the primary link or trunk group in a Layer 2 network using Spanning Tree Protocol. Normal recovery can take as long as 60 seconds, while the backup link transitions from Blocking to Listening to Learning and then Forwarding states. With Fast Uplink Convergence enabled, the switch immediately places the secondary path into Forwarding state, and sends multicasts of addresses in the forwarding database (FDB) and ARP table over the secondary link so that upstream switches can learn the new path. Configuration guidelines When you enable Fast Uplink Convergence, the switch software automatically makes the following configuration changes: • Increases the bridge priority to 65500 so that it does not become the root switch. • Increases the cost of all of the external ports by 3000, across all VLANs and Spanning Tree Groups. This ensures that traffic never flows through the switch to get to another switch unless there is no other path. When you disable Fast Uplink Convergence, the bridge priorities and path cost are set to their default values for all STP groups. Configuring Fast Uplink Convergence Use the following CLI commands to enable Fast Uplink Convergence on external ports: >> # /cfg/l2/upfast ena (Enable Fast Uplink convergence) >> Layer 2# apply (Make your changes active) >> Layer 2# save (Save for restore after reboot) Spanning Tree Protocol 61