Cisco 1601 Hardware Installation Guide - Page 173
Connecting Cisco Gigabit Ethernet High-Speed WAN Interface Cards to the Network
 |
View all Cisco 1601 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 173 highlights
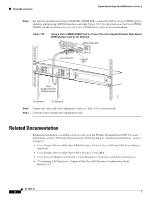
Gigabit Ethernet High-Speed WAN Interface Cards Connecting Cisco Gigabit Ethernet High-Speed WAN Interface Cards to the Network Figure 119 LC Connector 121498 Note Coarse wavelength-division multiplexing (CWDM) SFP transceivers are color-coded based on wavelength: gray (1470), violet (1490), blue (1510), green (1530), yellow (1550), orange (1570), red (1590), and brown (1610). Cisco Gigabit Ethernet high-speed WAN interface cards are designed for use in the following network design scenarios: • In metropolitan-area network (MAN) backbones for low-cost, high-speed, and long-distance connectivity • In multiprotocol WAN gateway routers for LANs • In same-building or same-campus wiring closets to achieve high-speed connectivity for high-demand network segments Tip For more information on possible network configurations using the Cisco Gigabit Ethernet high-speed WAN interface card, see Cisco product documentation. Connecting Cisco Gigabit Ethernet High-Speed WAN Interface Cards to the Network To connect the Cisco Gigabit Ethernet high-speed WAN interface card to the network, perform the following steps: Step 1 Confirm successful insertion of the SFP. Warning Because invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the aperture of the port when no fiber cable is connected, avoid exposure to laser radiation and do not stare into open apertures. Statement 125 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Confirm that the router is powered down. Remove optical port plugs from the installed SFP. Use the appropriate cable (see Table 35) to connect to the installed SFP. Note For short distances or loopbacks, network installations using 1000BASE-CWDM and 1000BASE-ZX SFPs may require 15-dBm attenuators to avoid over-powering the connection. Calculate the power budget for the connection to determine which attenuator to use. OL-12852-01 7