HP Integrity rx2800 Installation Guide, Windows Server 2008 R2 v7.0 - Page 82
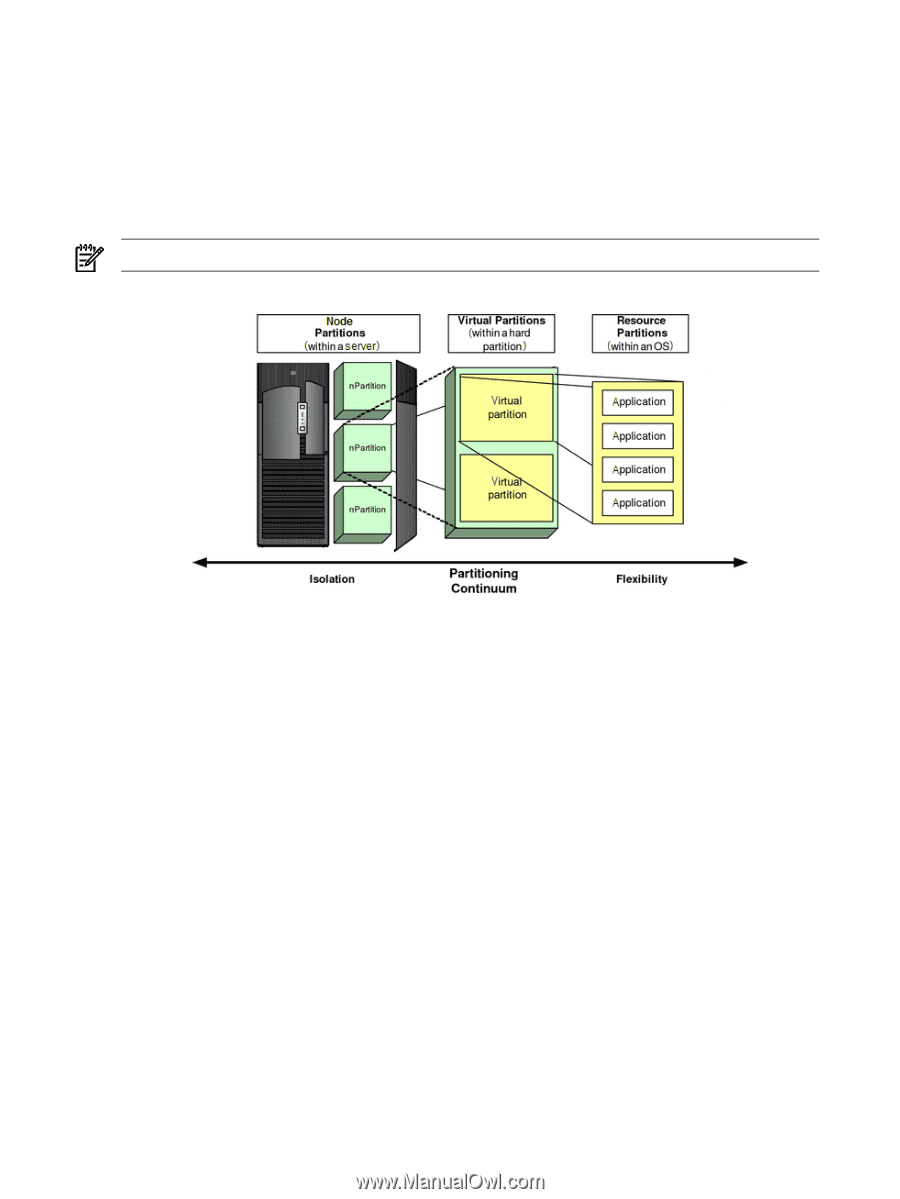
Getting to Know nPartitions, Partitioning Continuum, Cell Structure of nPartitions
 |
View all HP Integrity rx2800 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 82 highlights
Getting to Know nPartitions Partitions are physical or logical mechanisms for demarcating operational environments within a single system or across multiple systems. Partitioning lets you consolidate systems, allocate computing resources in response to fluctuations in demand, maximize resource use, and protect operating environments from disruptive events. Partitioning Continuum HP offers a continuum of partitioning technologies, as shown in Figure C-2. NOTE: Virtual Partitions are only available in systems running HP-UX. Figure C-2 Partitioning Continuum Node Partition Virtual Partition Resource Partition A node partition (nPartition) is a hard partition in a cell-based server. Cell-based servers can be configured as single large symmetric multiprocessors or as several independent systems. An nPartition has exclusive use of the memory, processor, and I/O resources belonging to the cells assigned to that partition and can execute its own operating system image. A virtual partition is a soft partition in a node or an nPartition. A virtual partition uses a subset of the system processor, memory, and I/O resources, and includes OS and application-related software. A resource partition is a soft partition in hard partitions or virtual partitions and is controlled by workload management services in the OS. Resource partitions enable an OS instance to allocate resources between competing applications. Cell Structure of nPartitions HP Integrity mid-range and high-end servers (rx7640, rx8640, and Superdome) are composed of cells or cell boards. A cell consists of up to four processor modules, contains memory modules (up to 32 DIMMs for Superdome cells, up to 16 DIMMs for rx7640 and rx8640 cells), and can connect to an I/O chassis that has I/O cards. A server cabinet can have several I/O chassis. Some cell-based servers support I/O expansion cabinets to provide additional I/O chassis. 82 nPartitioning