Netgear FVS338 FVS338 Reference Manual - Page 67
LAN Security Checks., VPN Pass through, Security, Firewall Rules, Attack, Checks, Attack Checks, Apply
 |
UPC - 606449037197
View all Netgear FVS338 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 67 highlights
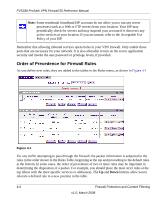
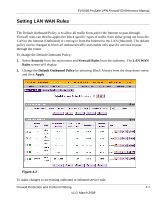
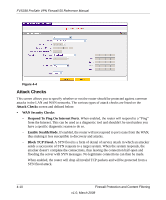
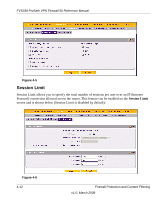
FVS338 ProSafe VPN Firewall 50 Reference Manual • LAN Security Checks. A UDP flood is a form of denial of service attack that can be initiated when one machine sends a large number of UDP packets to random ports on a remote host. As a result, the distant host will (1) check for the application listening at that port, (2) verify that no application is listening at that port, and then (3) reply with an ICMP Destination Unreachable packet. When the victimized system is flooded, it is forced to send many ICMP packets, eventually making it unreachable by other clients. The attacker may also spoof the IP address of the UDP packets, ensuring that the excessive ICMP return packets do not reach him, thus making the attacker's network location anonymous. If enabled, the router will not accept more than 20 simultaneous, active UDP connections from a single computer on the LAN. • VPN Pass through. When the router is in NAT mode, all packets going to the Remote VPN Gateway are first filtered through NAT and then encrypted per the VPN policy. For example, if a VPN Client or Gateway on the LAN side of this router wants to connect to another VPN endpoint on the WAN (placing this router between two VPN end points), encrypted packets will be sent to this router. Since this router filters the encrypted packets through NAT, the packets will become invalid unless VPN Pass through is enabled. When enabled, the VPN tunnel will pass the VPN traffic without any filtering. Tunnels can be - IPSec - PPTP - L2TP To select the appropriate checkbox for your requirement: 1. Select Security from the main menu, Firewall Rules from the submenu and then the Attack Checks tab. The Attack Checks screen will display. 2. Check the radio boxes of the Attack Checks you wish to initiate. 3. Click Apply to save your settings. Firewall Protection and Content Filtering v1.0, March 2008 4-11