D-Link DGS-3120-24TC Product Manual - Page 143
QoS,
 |
View all D-Link DGS-3120-24TC manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 143 highlights
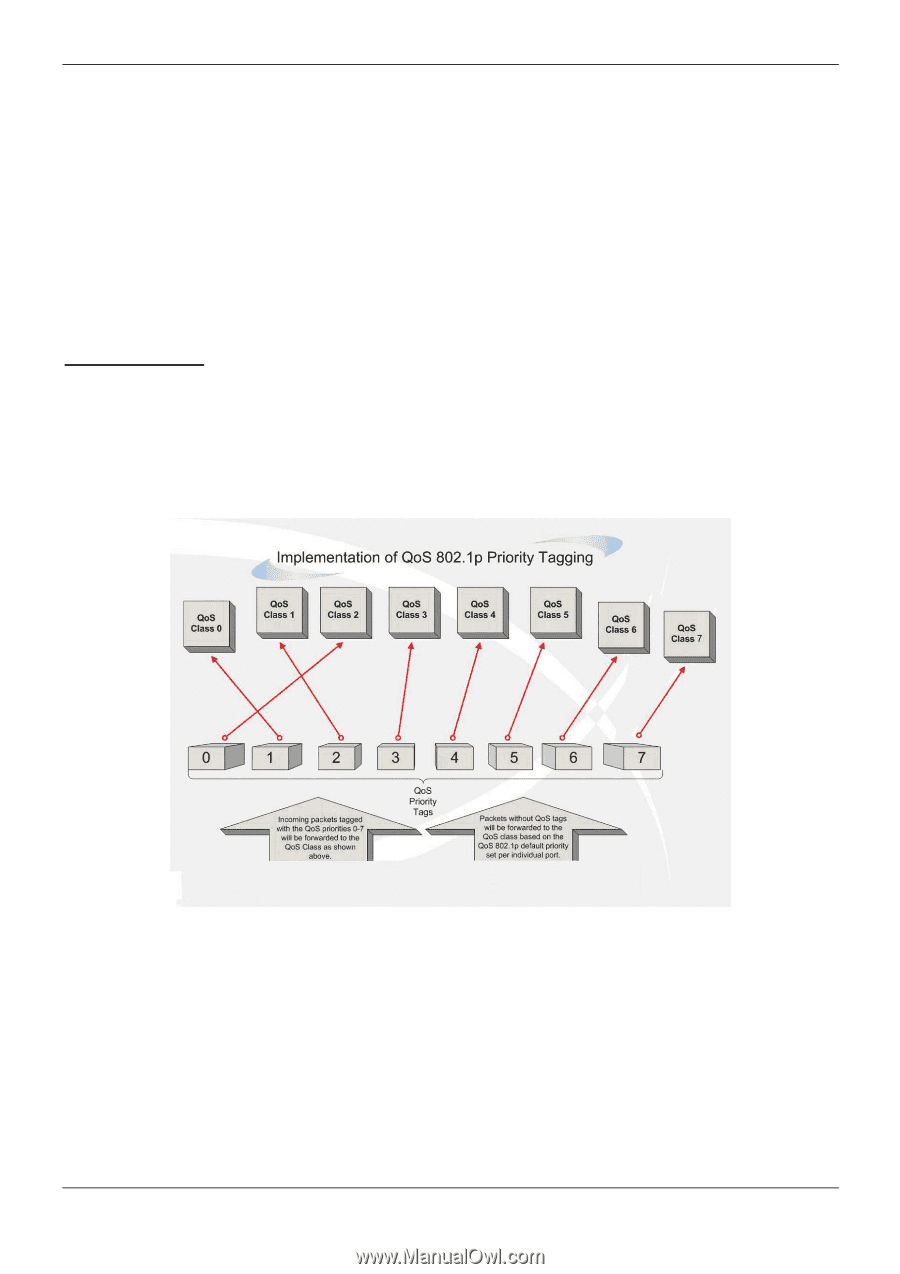
xStack® DGS-3120 Series Managed Switch Web UI Reference Guide Chapter 6 QoS 802.1p Settings Bandwidth Control Traffic Control Settings DSCP HOL Blocking Prevention Scheduling Settings The Switch supports 802.1p priority queuing Quality of Service. The following section discusses the implementation of QoS (Quality of Service) and benefits of using 802.1p priority queuing. Advantages of QoS QoS is an implementation of the IEEE 802.1p standard that allows network administrators a method of reserving bandwidth for important functions that require a large bandwidth or have a high priority, such as VoIP (voice-over Internet Protocol), web browsing applications, file server applications or video conferencing. Not only can a larger bandwidth be created, but other less critical traffic can be limited, so excessive bandwidth can be saved. The Switch has separate hardware queues on every physical port to which packets from various applications can be mapped to, and, in turn prioritized. View the following map to see how the Switch implements basic 802.1P priority queuing. Figure 6-1 Mapping QoS on the Switch The picture above shows the default priority setting for the Switch. Class-7 has the highest priority of the seven priority classes of service on the Switch. In order to implement QoS, the user is required to instruct the Switch to examine the header of a packet to see if it has the proper identifying tag. Then the user may forward these tagged packets to designated classes of service on the Switch where they will be emptied, based on priority. For example, let's say a user wishes to have a video conference between two remotely set computers. The administrator can add priority tags to the video packets being sent out, utilizing the Access Profile commands. Then, on the receiving end, the administrator instructs the Switch to examine packets for this tag, acquires the tagged packets and maps them to a class queue on the Switch. Then in turn, the administrator will set a priority for this queue so that will be emptied before any other packet is forwarded. This result in the end user receiving all packets sent as quickly as possible, thus prioritizing the queue and allowing for an uninterrupted stream of packets, which optimizes the use of bandwidth available for the video conference. 135