HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Security Configuration Gui - Page 130
Configuring secure MAC addresses
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 130 highlights
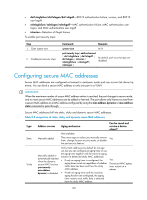
• dot1xlogfailure/dot1xlogon/dot1xlogoff-802.1X authentication failure, success, and 802.1X user logoff. • ralmlogfailure/ralmlogon/ralmlogoff-MAC authentication failure, MAC authentication user logon, and MAC authentication user logoff. • intrusion-Detection of illegal frames. To enable port security traps: Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Enable port security traps. Command Remarks system-view N/A port-security trap { addresslearned | dot1xlogfailure | dot1xlogoff | dot1xlogon | intrusion | ralmlogfailure | ralmlogoff | ralmlogon } By default, port security traps are disabled. Configuring secure MAC addresses Secure MAC addresses are configured or learned in autoLearn mode and can survive link down/up events. You can bind a secure MAC address to only one port in a VLAN. IMPORTANT: When the maximum number of secure MAC address entries is reached, the port changes to secure mode, and no more secure MAC addresses can be added or learned. The port allows only frames sourced from a secure MAC address or a MAC address configured by using the mac-address dynamic or mac-address static command to pass through. Secure MAC addresses fall into static, sticky and dynamic secure MAC addresses. Table 9 A comparison of static, sticky, and dynamic secure MAC addresses Type Static Sticky Address sources Aging mechanism Can be saved and survive a device reboot? Manually added Not available. They never age out unless you manually remove Yes. them, change the port security mode, or disable the port security feature. Manually added or automatically learned when the dynamic secure MAC function (port-security mac-address dynamic) is disabled. Sticky MAC addresses by default do not age out, but you can configure an aging timer or use the aging timer together with the inactivity aging function to delete old sticky MAC addresses: • If only an aging timer is configured, the aging timer counts up regardless of whether traffic data has been sent from the sticky MAC address. • If both an aging timer and the inactivity aging function are configured, the aging timer restarts once traffic data is detected from the sticky MAC address. Yes. The secure MAC aging timer restarts at a reboot. 120