HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Security Configuration Gui - Page 19
Domain-based user management
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 19 highlights
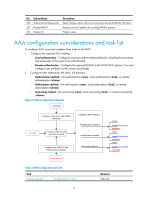
9. The user enters the password. 10. After receiving the login password, the HWTACACS client sends the HWTACACS server a continue-authentication packet that carries the login password. 11. The HWTACACS server sends back an authentication response to indicate that the user has passed authentication. 12. The HWTACACS client sends the user an authorization request packet to the HWTACACS server. 13. The HWTACACS server sends back the authorization response, indicating that the user is now authorized. 14. Knowing that the user is now authorized, the HWTACACS client pushes its configuration interface to the user. 15. The HWTACACS client sends a start-accounting request to the HWTACACS server. 16. The HWTACACS server sends back an accounting response, indicating that it has received the start-accounting request. 17. The user logs off. 18. The HWTACACS client sends a stop-accounting request to the HWTACACS server. 19. The HWTACACS server sends back a stop-accounting response, indicating that the stop-accounting request has been received. Domain-based user management A NAS manages users based on Internet service provider (ISP) domains. On a NAS, each user belongs to one ISP domain. A NAS determines the ISP domain a user belongs to by the username entered by the user at login, as shown in Figure 7. Figure 7 Determining the ISP domain of a user by the username NAS A user enters the username in the form of userid@domain-name or userid Username contains Yes @domain-name? No Use the AAA methods and attributes of the default domain for the user Use the AAA methods and attributes of domain domain-name for the user The authentication, authorization, and accounting of a user depends on the AAA methods configured for the domain to which the user belongs. If no specific AAA methods are configured for the domain, the default methods are used. By default, a domain uses local authentication, local authorization, and local accounting. AAA allows you to manage users based on their access types: • LAN users-Users on a LAN who must pass 802.1X or MAC address authentication to access the network. • Login users-Users who want to log in to the switch, including SSH users, Telnet users, Web users, FTP users, and terminal users. 9