HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Security Configuration Gui - Page 168
PKI applications, PKI configuration task list
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 168 highlights
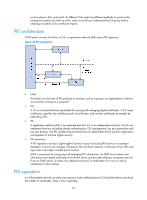
1. An entity submits a certificate request to the RA. 2. The RA reviews the identity of the entity and then sends the identity information and the public key with a digital signature to the CA. 3. The CA verifies the digital signature, approves the application, and issues a certificate. 4. The RA receives the certificate from the CA, sends it to the LDAP server or other distribution point to provide directory navigation service, and notifies the entity that the certificate is successfully issued. 5. The entity retrieves the certificate. With the certificate, the entity can communicate with other entities safely through encryption and digital signature. 6. The entity makes a request to the CA when it needs to revoke its certificate. The CA approves the request, updates the CRLs and publishes the CRLs on the LDAP server or other distribution point. PKI applications The PKI technology can satisfy the security requirements of online transactions. As an infrastructure, PKI has a wide range of applications. Here are some application examples. • VPN A virtual private network (VPN) is a private data communication network built on the public communication infrastructure. A VPN can leverage network layer security protocols (for instance, IPsec) in conjunction with PKI-based encryption and digital signature technologies for confidentiality. • Secure email Emails require confidentiality, integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation. PKI can address these needs. The secure email protocol that is developing rapidly is Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (S/MIME), which is based on PKI and allows for transfer of encrypted mails with signature. • Web security For Web security, two peers can establish an SSL connection first for transparent and secure communications at the application layer. With PKI, SSL enables encrypted communications between a browser and a server. Both of the communication parties can verify each other's identity through digital certificates. PKI configuration task list Task Configuring an entity DN Configuring a PKI domain Submitting a PKI certificate request • Submitting a certificate request in auto mode • Submitting a certificate request in manual mode Retrieving a certificate manually Configuring PKI certificate verification Destroying a local RSA key pair 158 Remarks Required. Required. Required. Use either approach. Optional. Optional. Optional.