HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Security Configuration Gui - Page 226
Configuring SSL, Overview, SSL security mechanism, SSL protocol stack
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 226 highlights
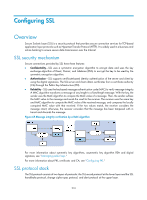
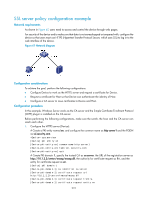
Configuring SSL Overview Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a security protocol that provides secure connection services for TCP-based application layer protocols such as Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). It is widely used in e-business and online banking to ensure secure data transmission over the Internet. SSL security mechanism Secure connections provided by SSL have these features: • Confidentiality-SSL uses a symmetric encryption algorithm to encrypt data and uses the key exchange algorithm of Rivest, Shamir, and Adelman (RSA) to encrypt the key to be used by the symmetric encryption algorithm. • Authentication-SSL supports certificate-based identity authentication of the server and client by using the digital signatures. The SSL server and client obtain certificates from a certificate authority (CA) through the Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). • Reliability-SSL uses the key-based message authentication code (MAC) to verify message integrity. A MAC algorithm transforms a message of any length to a fixed-length message. With the key, the sender uses the MAC algorithm to compute the MAC value of a message. Then, the sender suffixes the MAC value to the message and sends the result to the receiver. The receiver uses the same key and MAC algorithm to compute the MAC value of the received message, and compares the locally computed MAC value with that received. If the two values match, the receiver considers the message intact; otherwise, the receiver considers that the message has been tampered with in transit and discards the message. Figure 65 Message integrity verification by a MAC algorithm For more information about symmetric key algorithms, asymmetric key algorithm RSA and digital signature, see "Managing public keys." For more information about PKI, certificate, and CA, see "Configuring PKI." SSL protocol stack The SSL protocol consists of two layers of protocols: the SSL record protocol at the lower layer and the SSL handshake protocol, change cipher spec protocol, and alert protocol at the upper layer. 216