HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Security Configuration Gui - Page 40
Enabling the trap function for RADIUS, Enabling the RADIUS listening port of the RADIUS client
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 40 highlights
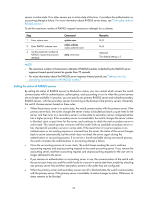
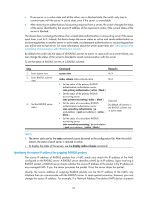
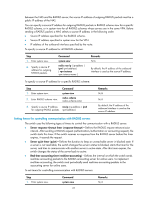
NOTE: Whether interpretation of RADIUS class attribute as CAR parameters is supported depends on two factors: • Whether the switch supports CAR parameters assignment. • Whether the RADIUS server supports assigning CAR parameters through the class attribute. Enabling the trap function for RADIUS With the trap function, a NAS sends a trap message when either of the following events occurs: • The status of a RADIUS server changes. If a NAS receives no response to an accounting or authentication request before the specified maximum number of RADIUS request transmission attempts is exceeded, it considers the server unreachable, sets the status of the server to block and sends a trap message. If the NAS receives a response from a RADIUS server that it considers unreachable, the NAS considers that the RADIUS server is reachable again, sets the status of the server to active, and sends a trap message. • The ratio of the number of failed transmission attempts to the total number of authentication request transmission attempts reaches the threshold. This threshold ranges from 1% to 100% and defaults to 30%. This threshold can only be configured through the MIB. The failure ratio is generally small. If a trap message is triggered because the failure ratio is higher than the threshold, troubleshoot the configuration on and the communication between the NAS and the RADIUS server. To enable the trap function for RADIUS: Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Enable the trap function for RADIUS. Command system-view radius trap { accounting-server-down | authentication-error-threshold | authentication-server-down } Remarks N/A Disabled by default. Enabling the RADIUS listening port of the RADIUS client Only after you enable the RADIUS listening port of a RADIUS client, can the client receive and send RADIUS packets. If RADIUS is not required, disable the RADIUS listening port to avoid attacks that exploit RADIUS packets. To enable the RADIUS listening port of a RADIUS client: Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Enable the RADIUS listening port of a RADIUS client. Command system-view radius client enable Remarks N/A Optional. Enabled by default. Setting the DSCP value for RADIUS protocol packets An IP packet originally uses an eight-bit field to identify the service type, which is known as "Type of Service (ToS)" in IPv4 or "traffic class" in IPv6. RFC 2474 redefines the first six bits of the field as a differentiated services code point, called the DSCP field. Network devices use the DSCP value to determine the class of each packet for transmission. Different transmission priorities can be assigned to packet classes. 30