HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Security Configuration Gui - Page 17
HWTACACS, Differences between HWTACACS and RADIUS, Basic HWTACACS message exchange process
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 17 highlights
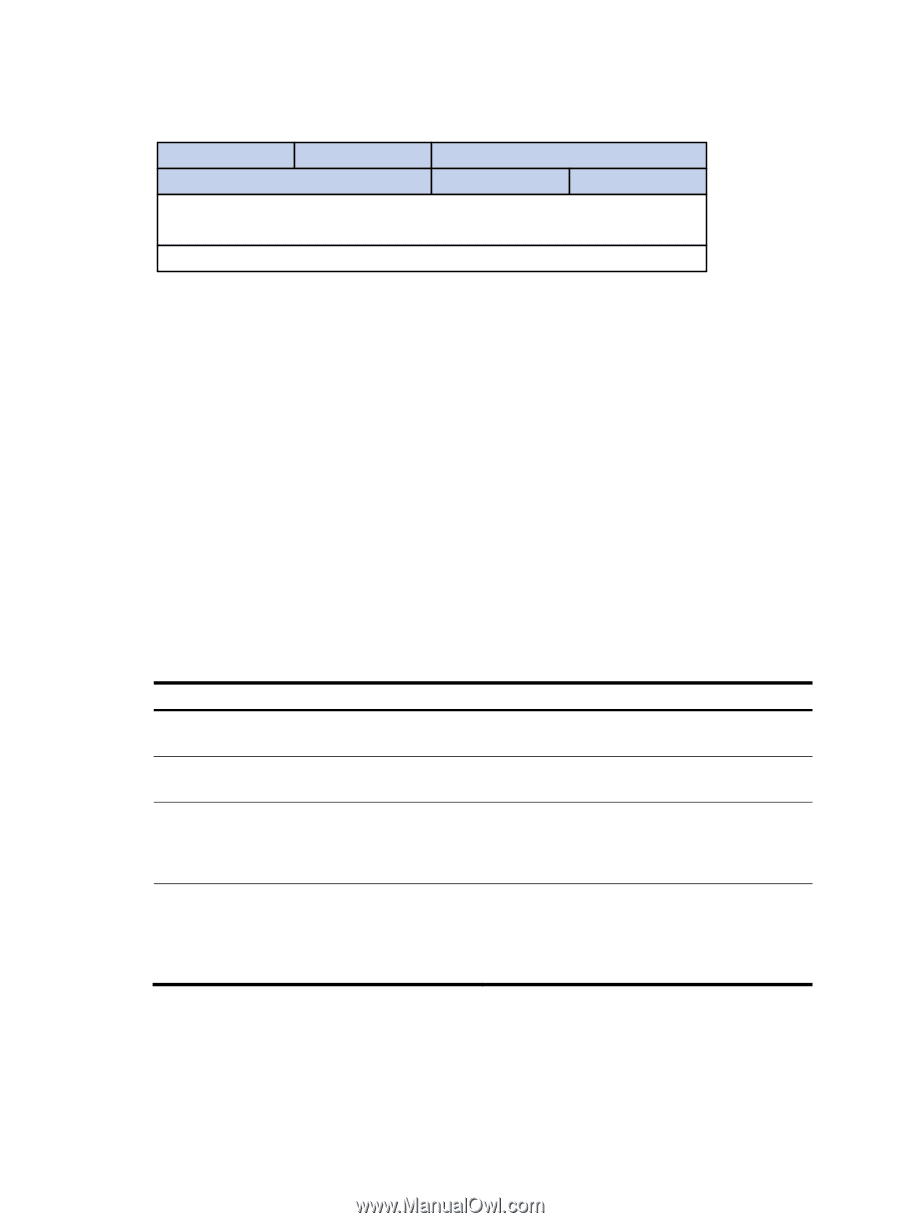
Figure 5 Segment of a RADIUS packet containing an extended attribute 0 7 Type 15 Length 23 31 Vendor-ID Vendor-ID (continued) Vendor-Type Vendor-Length Vendor-Data (Specified attribute value......) ...... HWTACACS HW Terminal Access Controller Access Control System (HWTACACS) is an enhanced security protocol based on TACACS (RFC 1492). Similar to RADIUS, it uses a client/server model for information exchange between the NAS and the HWTACACS server. HWTACACS typically provides AAA services for Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) users, Virtual Private Dial-up Network (VPDN) users, and terminal users. In a typical HWTACACS scenario, some terminal users log in to the NAS for operations. Working as the HWTACACS client, the NAS sends the usernames and passwords of the users to the HWTACACS sever for authentication. After passing authentication and being authorized, the users log in to the switch and performs operations, and the HWTACACS server records the operations that each user performs. Differences between HWTACACS and RADIUS HWTACACS and RADIUS both provide authentication, authorization, and accounting services. They have many features in common, such as using a client/server model, using shared keys for user information security, and providing flexibility and extensibility. Table 3 Primary differences between HWTACACS and RADIUS HWTACACS RADIUS Uses TCP, providing more reliable network transmission. Uses UDP, providing higher transport efficiency. Encrypts the entire packet except for the HWTACACS Encrypts only the user password field in an header. authentication packet. Protocol packets are complicated and authorization is independent of authentication. Authentication and authorization can be deployed on different HWTACACS servers. Protocol packets are simple and the authorization process is combined with the authentication process. Supports authorization of configuration commands. Which commands a user can use depends on both the user level and the AAA authorization. A user can use only commands that are at, or lower than, the user level and authorized by the HWTACACS server. Does not support authorization of configuration commands. Which commands a user can use solely depends on the level of the user. A user can use all the commands at, or lower than, the user level. Basic HWTACACS message exchange process The following example describes how HWTACACS performs user authentication, authorization, and accounting for a Telnet user. 7