HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Network Management and Monitoring Com - Page 166
Examples, Table 41, Command output
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 166 highlights
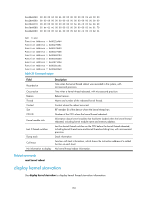
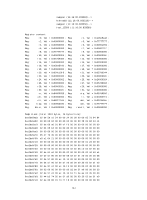
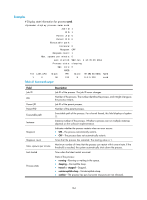
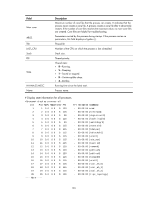
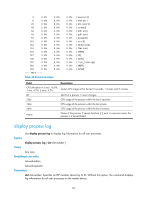
Examples # Display state information for process scmd. display process name scmd Job ID: 1 PID: 1 Parent JID: 0 Parent PID: 0 Executable path: - Instance: 0 Respawn: OFF Respawn count: 1 Max. spawns per minute: 0 Last started: Wed Jun 1 14:45:46 2011 Process state: sleeping Max. core: 0 ARGS: - TID LAST_CPU Stack PRI State HH:MM:SS:MESC Name 1 0 0K 120 S 0:0:5:220 scmd Table 41 Command output Field Job ID PID Parent JID Parent PID Executable path Instance Respawn Respawn count Max. spawns per minute Last started Process state Description Job ID of the process. The job ID never changes. Number of the process. The number identifies the process, and it might change as the process restarts. Job ID of the parent process. Number of the parent process. Executable path of the process. For a kernel thread, this field displays a hyphen (-). Instance number of the process. Whether a process can run multiple instances depends on the software implementation. Indicates whether the process restarts when an error occurs: • ON-The process automatically restarts. • OFF-The process does not automatically restarts. Times that the process has restarted. The starting value is 1. Maximum number of times that the process can restart within one minute. If the threshold is reached, the system automatically shuts down the process. Time when the latest restart occurred. State of the process: • running-Running or waiting in the queue. • sleeping-Interruptible sleep. • traced or stopped-Stopped. • uninterruptible sleep-Uninterruptible sleep. • zombie-The process has quit, but some resources are not released. 164