HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Network Management and Monitoring Com - Page 175
monitor kernel deadloop enable
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 175 highlights
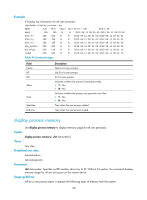
0xb7e30200 0xb7e30210 0xb7e30220 0xb7e30230 Related commands • display process memory heap • display process memory heap address monitor kernel deadloop enable Use monitor kernel deadloop enable to enable kernel thread deadloop detection. Use undo monitor kernel deadloop enable to disable kernel thread deadloop detection. Syntax monitor kernel deadloop enable [ slot slot-number ] undo monitor kernel deadloop enable [ slot slot-number ] Default Kernel thread deadloop detection is disabled. Views System view Predefined user roles network-admin Parameters slot slot-number: Specifies an IRF member device by its ID. If you do not specify this option, the master device is specified. Usage guidelines Kernel threads share resources in kernel space. If a kernel thread monopolizes the CPU for a long time, other threads cannot run, resulting in a deadloop. This command enables the device to detect deadloops. If a thread occupies the CPU for a specific interval, the device considers that a deadloop has occurred. It outputs a deadloop message and reboots to remove the deadloop. Inappropriate use of this command can cause service problems or system breakdown. Make sure you understand the impact of this command on your network before you use it. Examples # Enable kernel thread deadloop detection. system-view [Sysname] monitor kernel deadloop enable Related commands • display kernel deadloop • display kernel deadloop configuration • monitor kernel deadloop exclude-thread • monitor kernel deadloop time 173