HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Network Management and Monitoring Com - Page 170
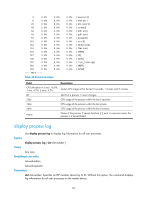
display process memory
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 170 highlights
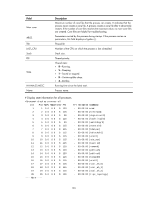
Examples # Display log information for all user processes. display process log Name JID PID Abort Core Start-time End-time mdcd 135 135 N N 2012-06-11 09:31:00 2012-06-11 09:31:00 knotify 156 156 N N 2012-06-11 09:31:02 2012-06-11 09:31:02 knotify 158 158 N N 2012-06-11 09:31:02 2012-06-11 09:31:02 knotify 195 195 N N 2012-06-11 09:31:03 2012-06-11 09:31:03 pkg_update 203 203 N N 2012-06-11 09:31:06 2012-06-11 09:31:06 autocfgd 219 219 N N 2012-06-11 09:31:13 2012-06-11 09:31:13 comsh 202 202 N N 2012-06-11 09:31:05 2012-06-11 09:31:13 Table 44 Command output Field Name JID PID Abort Core Start-time End-time Description Name of a user process. Job ID of a user process. ID of a user process. Indicates whether the process exited abnormally: • Y-Yes. • N-No. Indicates whether the process can generate core files: • Y-Yes. • N-No. Time when the user process started. Time when the user process ended. display process memory Use display process memory to display memory usage for all user processes. Syntax display process memory [ slot slot-number ] Views Any view Predefined user roles network-admin network-operator Parameters slot slot-number: Specifies an IRF member device by its ID. Without this option, the command displays memory usage for all user processes on the master device. Usage guidelines When a user process starts, it requests the following types of memory from the system: 168