HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Network Management and Monitoring Con - Page 10
Prerequisites, Using a tracert command to identify failed or all nodes in a path, Tracert example
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 10 highlights
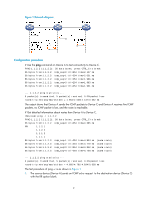
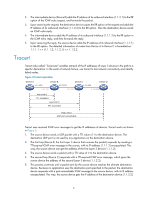
6. The source device thinks that the packet has reached the destination device after receiving the port-unreachable ICMP message, and the path to the destination device is 1.1.1.2 to 1.1.2.2 to 1.1.3.2. Prerequisites Before you use a tracert command, perform the tasks in this section. For an IPv4 network: • Enable sending of ICMP timeout packets on the intermediate devices (devices between the source and destination devices). If the intermediate devices are HP devices, execute the ip ttl-expires enable command on the devices. For more information about this command, see Layer 3-IP Services Command Reference. • Enable sending of ICMP destination unreachable packets on the destination device. If the destination device is an HP device, execute the ip unreachables enable command. For more information about this command, see Layer 3-IP Services Command Reference. For an IPv6 network: • Enable sending of ICMPv6 timeout packets on the intermediate devices (devices between the source and destination devices). If the intermediate devices are HP devices, execute the ipv6 hoplimit-expires enable command on the devices. For more information about this command, see Layer 3-IP Services Command Reference. • Enable sending of ICMPv6 destination unreachable packets on the destination device. If the destination device is an HP device, execute the ipv6 unreachables enable command. For more information about this command, see Layer 3-IP Services Command Reference. Using a tracert command to identify failed or all nodes in a path Execute tracert commands in any view. Task Command • For IPv4 networks: tracert [ -a source-ip | -f first-ttl | -m max-ttl | -p port | -q packet-number Display the routes from source to | -vpn-instance vpn-instance-name | -w timeout ] * host destination. • For IPv6 networks: tracert ipv6 [ -f first-hop| -m max-hops | -p port | -q packet-number | -vpn-instance vpn-instance-name | -w timeout ] * host Tracert example Network requirements As shown in Figure 3, Device A failed to Telnet Device C. Test the network connectivity between Device A and Device C. If they cannot reach each other, locate the failed nodes in the network. 4