HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Network Management and Monitoring Con - Page 108
Monitoring kernel threads, Configuring kernel thread deadloop detection
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 108 highlights
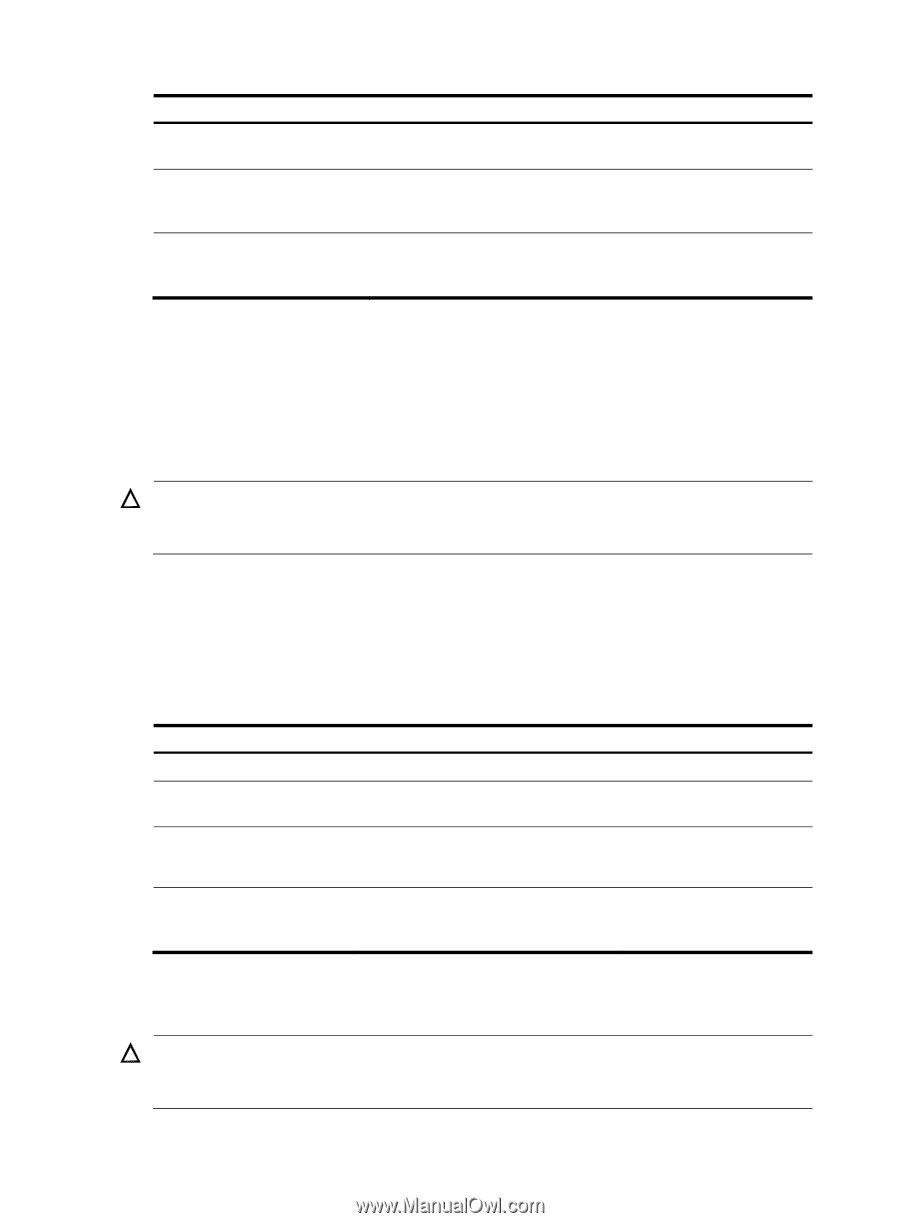
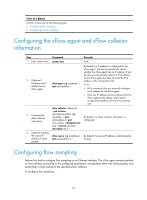
Task Command Display heap memory usage for a user process. display process memory heap job job-id [ verbose ] [ slot slot-number ] Display the addresses of memory blocks with a specified size used by a user process. display process memory heap job job-id size memory-size [ offset offset-size ] [ slot slot-number ] Display memory content starting from a specified memory block for a user process. display process memory heap job job-id address starting-address length memory-length [ slot slot-number ] Monitoring kernel threads Tasks in this section help you quickly identify thread deadloop and starvation problems and their causes. Configuring kernel thread deadloop detection CAUTION: Inappropriate configuration of kernel thread deadloop detection can cause service problems or system breakdown. Make sure you understand the impact of this configuration on your network before you do it. Kernel threads share resources. If a kernel thread monopolizes the CPU, other threads cannot run, resulting in a deadloop. This feature enables the device to detect deadloops. If a thread occupies the CPU for a specific interval, the device considers that a deadloop has occurred. It generates a deadloop message and reboots to remove the deadloop. To configure kernel thread deadloop detection: Step Command Remarks 1. Enter system view. system-view N/A 2. Enable kernel thread deadloop detection. monitor kernel deadloop enable [ slot slot-number ] By default, the function is disabled. 3. (Optional.) Set the interval for identifying a kernel thread deadloop. monitor kernel deadloop time interval [ slot slot-number ] The default is 60 seconds. 4. (Optional.) Disable kernel thread deadloop detection monitor kernel deadloop exclude-thread for a kernel thread. tid [ slot slot-number ] After enabled, kernel thread deadloop detection monitors all kernel threads by default. Configuring kernel thread starvation detection CAUTION: Inappropriate configuration of kernel thread starvation detection can cause service problems or system breakdown. Make sure you understand the impact of this configuration on your network before you do it. 102