HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Network Management and Monitoring Con - Page 129
Traffic mirroring configuration example, Network requirements, Configuration procedure
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 129 highlights
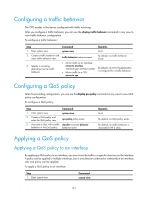
Traffic mirroring configuration example Network requirements As shown in Figure 38, different departments of a company use IP addresses on different subnets. The marketing and technical departments use the IP addresses on subnets 192.168.1.0/24 and 192.168.2.0/24, respectively. The working hour of the company is from 8:00 to 18:00 on weekdays. Configure traffic mirroring so that the server can monitor the traffic that the technical department sends to access the Internet, and IP traffic that the technical department sends to the marketing department. Figure 38 Network diagram Configuration procedure # Create a working hour range named work, in which the working hour is from 8:00 to 18:00 on weekdays. system-view [DeviceA] time-range work 8:00 to 18:00 working-day # Create ACL 3000 to allow packets from the technical department to access the Internet and to the marketing department during working hours. [DeviceA] acl number 3000 [DeviceA-acl-adv-3000] rule permit tcp source 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 destination-port eq www [DeviceA-acl-adv-3000] rule permit ip source 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 destination 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 time-range work [DeviceA-acl-adv-3000] quit # Create traffic class tech_c, and configure the match criterion as ACL 3000. [DeviceA] traffic classifier tech_c [DeviceA-classifier-tech_c] if-match acl 3000 [DeviceA-classifier-tech_c] quit 123