HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Network Management and Monitoring Con - Page 16
Association modes, Working process, Principle, Application scenario
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 16 highlights
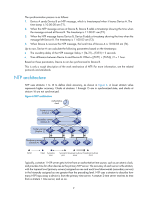
To ensure time accuracy and availability, you can specify multiple NTP servers for a device. The device selects an optimal NTP server as the clock source based on parameters such as stratum. The clock that the device selects is called the reference source. For more information about clock selection, see the related protocols and standards. If the devices in a network cannot synchronize to an authoritative time source, you can select a device that has a relatively accurate clock from the network, and use the local clock of the device as the reference clock to synchronize other devices in the network. Association modes NTP supports the following association modes: • Client/server mode • Symmetric active/passive mode • Broadcast mode • Multicast mode Table 1 NTP association modes Mode Client/server Working process On the client, specify the IP address of the NTP server. A client sends a clock synchronization message to the NTP servers. Upon receiving the message, the servers automatically operate in server mode and send a reply. If the client can be synchronized to multiple time servers, it selects an optimal clock and synchronizes its local clock to the optimal reference source after receiving the replies from the servers. Principle A client can be synchronized to a server, but a server cannot be synchronized to a client. Application scenario As Figure 6 shows, this mode is intended for configurations where devices of a higher stratum are synchronized to devices with a lower stratum. 10