HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Network Management and Monitoring Con - Page 37
Configuration procedure, Network diagram
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 37 highlights
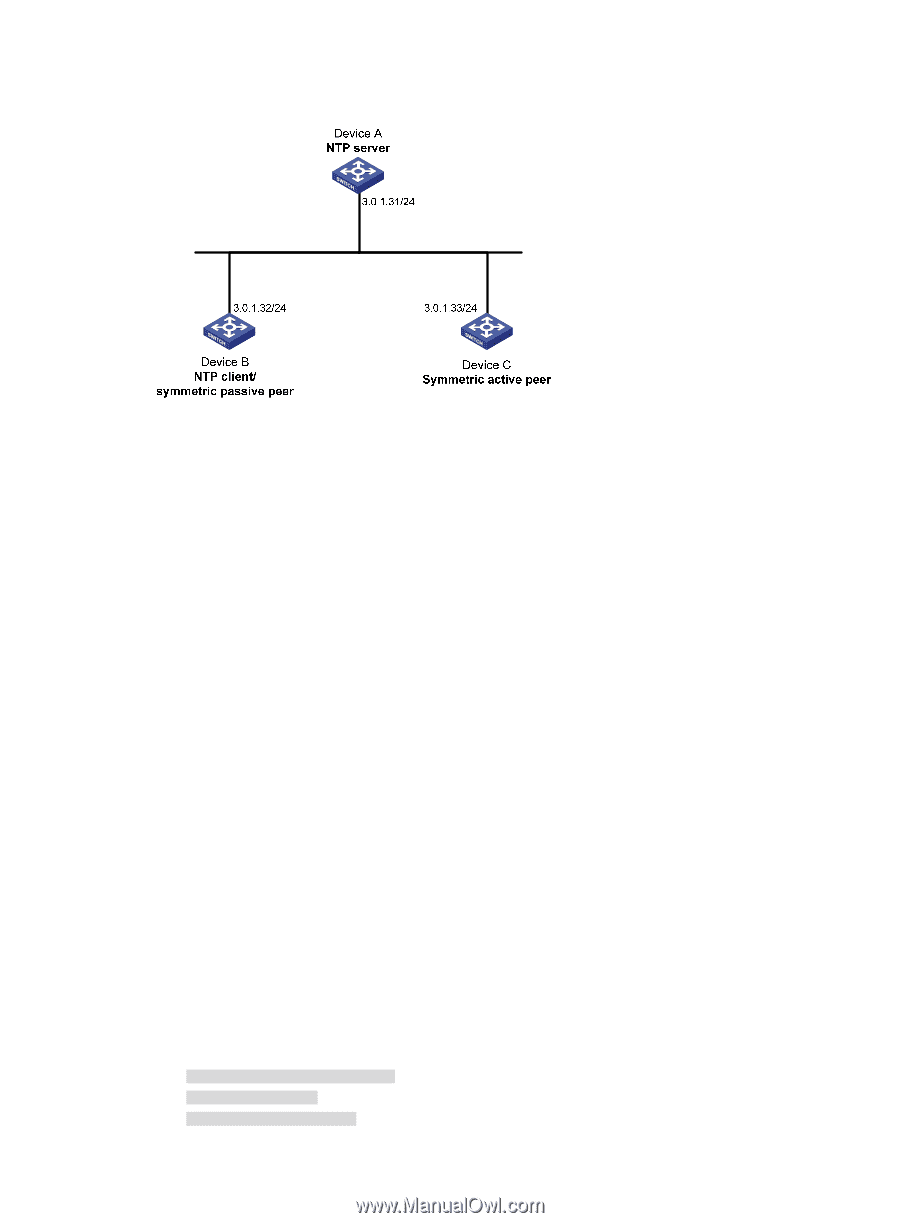
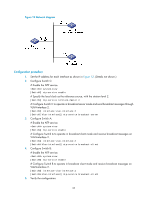
Figure 10 Network diagram Configuration procedure 1. Set the IP address for each interface as shown in Figure 10. (Details not shown.) 2. Configure Device A: # Enable the NTP service. system-view [DeviceA] ntp-service enable # Specify the local clock as the reference source, with the stratum level 3. [DeviceA] ntp-service refclock-master 3 3. Configure Device B: # Enable the NTP service. [DeviceB] ntp-service enable # Specify Device A as the NTP server of Device B. [DeviceB] ntp-service unicast-server 3.0.1.31 4. Configure Device C: # Enable the NTP service. system-view [DeviceC] ntp-service enable # Specify the local clock as the reference source, with the stratum level 2. [DeviceC] ntp-service refclock-master 2 # Configure Device B as a symmetric passive peer. [DeviceC] ntp-service unicast-peer 3.0.1.32 5. Verify the configuration: # After the configuration, Device B has two time servers Device A and Device C. Device C has a lower stratum level than Device A, so Device B selects Device C as a reference clock to synchronize to Device C. After synchronization, view the status of Device B. The output shows that Device B has been synchronized to Device C. [DeviceB] display ntp-service status Clock status: synchronized Clock stratum: 3 System peer: 3.0.1.33 31