HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Network Management and Monitoring Con - Page 81
Configuring the SNMP agent to send notifications to a host, Configuration guidelines
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 81 highlights
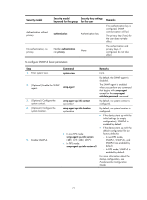
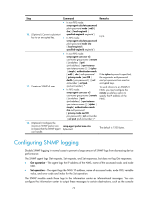
Step 4. Enable link state notifications. Command enable snmp trap updown Remarks By default, link state notifications are enabled. Configuring the SNMP agent to send notifications to a host You can configure the SNMP agent to send notifications as traps or informs to a host, typically an NMS, for analysis and management. Traps are less reliable and use fewer resources than informs, because an NMS does not send an acknowledgement when it receives a trap. Configuration guidelines When network congestion occurs or the destination is not reachable, the SNMP agent buffers notifications in a queue. You can configure the queue size and the notification lifetime (the maximum time that a notification can stay in the queue). A notification is deleted when its lifetime expires. When the notification queue is full, the oldest notifications are automatically deleted. You can extend standard linkUp/linkDown notifications to include interface description and interface type, but must make sure that the NMS supports the extended SNMP messages. To send informs, make sure: • The SNMP agent and the NMS use SNMPv2c or SNMPv3. • If SNMPv3 is used, you must configure the SNMP engine ID of the NMS when you configure SNMPv3 basic settings. Also, specify the IP address of the SNMP engine when you create the SNMPv3 user. Configuration prerequisites Configure the SNMP agent with the same basic SNMP settings as the NMS. If SNMPv1 or SNMPv2c is used, you must configure a community name. If SNMPv3 is used, you must configure an SNMPv3 user, a MIB view, and a remote SNMP engine ID associated with the SNMPv3 user for notifications. The SNMP agent and the NMS can reach each other. Configuration procedure To configure the SNMP agent to send notifications to a host: Step 1. Enter system view. Command system-view Remarks N/A 75