HP rp5800 Maintenance & Service Guide HP rp5800 Retail System - Page 16
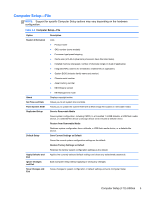
Computer Setup—Storage, Table 2-3
 |
View all HP rp5800 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 16 highlights
Computer Setup-Storage NOTE: Support for specific Computer Setup options may vary depending on the hardware configuration. Table 2-3 Computer Setup-Storage Option Description Device Configuration Lists all installed BIOS-controlled storage devices. When a device is selected, detailed information and options are displayed. The following options may be presented: CD-ROM: Size, model, firmware version, serial number, connector color, SMART, emulation type. Hard Disk: Size, model, firmware version, serial number. ● Translation Mode (ATA disks only) Lets you select the translation mode to be used for the device. This enables the BIOS to access disks partitioned and formatted on other systems and may be necessary for users of older versions of UNIX (e.g., SCO UNIX version 3.2). Options are Automatic, Bit-Shift, LBA Assisted, User, and Off. Available only when the drive translation mode is set to User, allows you to specify the parameters (logical cylinders, heads, and sectors per track) used by the BIOS to translate disk I/O requests (from the operating system or an application) into terms the hard drive can accept. Logical cylinders may not exceed 1024. The number of heads may not exceed 256. The number of sectors per track may not exceed 63. CAUTION: Ordinarily, the translation mode selected automatically by the BIOS should not be changed. If the selected translation mode is not compatible with the translation mode that was active when the disk was partitioned and formatted, the data on the disk will be inaccessible. Default Values SATA Defaults See Translation Mode above for details. 6 Chapter 2 Computer Setup (F10) Utility