D-Link DGS-3308FG Product Manual - Page 101
Static Router Port
 |
UPC - 790069239373
View all D-Link DGS-3308FG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 101 highlights
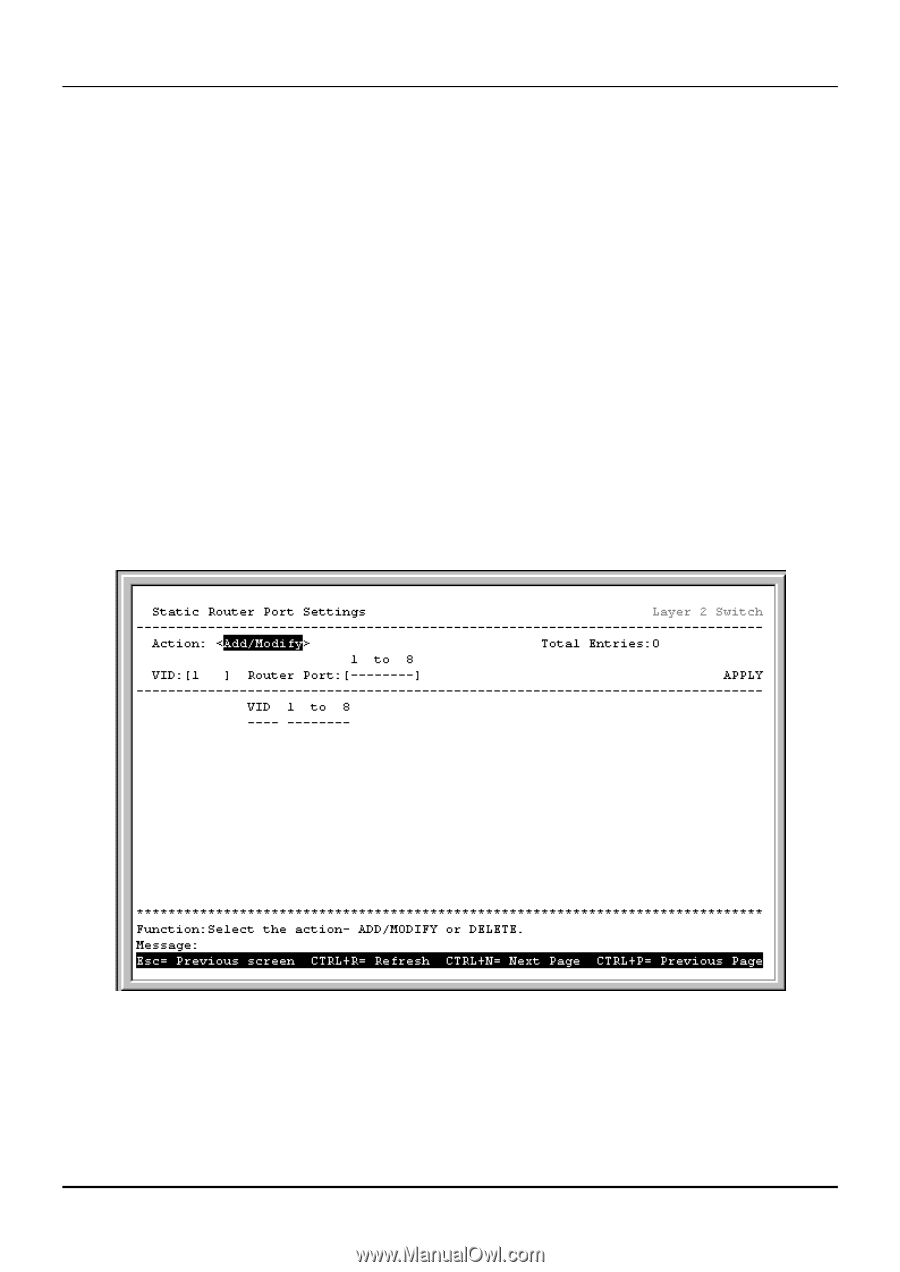
8-port Gigabit Ethernet Switch User's Guide Static Router Port Note: There is no difference between the setup of a 'router port' in Layer 2 Only mode and in IP Routing mode. Note: A router port allows UDP multicast and IGMP packets to be forwarded to a designated port on the switch regardless of VLAN configuration. Note: A router port functions within layer 2 of the OSI model. This section is repeated in the Layer 3 Multicasting section of this manual below because of the possible confusion caused by the term 'router port' when compared to a traditional router. A static router port is a port that has a router attached to it. Generally, this router would have a connection to a WAN or to the Internet. Establishing a router port will allow multicast packets coming from the router to be propagated through the network, as well as allowing multicast messages coming from the network to be propagated to the router. The purpose of a router port is to enable UDP multicast packets, and IGMP multicast group membership messages to reach multiple ports of a multicast-enabled router. Routers do not implement IGMP snooping or transmit/forward IGMP report packets. Thus, forwarding all IP UDP multicast packets to a static router port on the DGS-3308 guarantees that all ports of a multicast-enabled router - attached to the DGS-3308- can reach all multicast group members through the attached router's other ports. To setup a static router port, highlight Static Router Port Settings from the Multicasting Menu and press Enter. Figure 6-38. Static Router Port Settings screen Note: All IGMP Report packets will be forwarded to the router port. Note: IGMP queries (from the router port) will be flooded to all ports. Note: All UDP multicast packets will be forwarded to the router port. Because routers do not send IGMP reports or implement IGMP snooping, a multicast-enabled router connected to the router 91