D-Link DGS-3308FG Product Manual - Page 186
STP Port Settings screen
 |
UPC - 790069239373
View all D-Link DGS-3308FG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 186 highlights
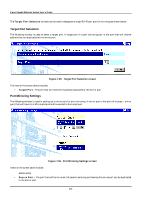
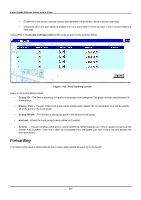
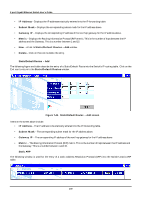
8-port Gigabit Ethernet Switch User's Guide Figure 7-40. STP Port Settings screen Items on the screen above include: • Cost - A port cost can be set between 1 and 65535. The lower the cost, the greater the probability the port will be chosen as the designated port (chosen to forward packets). • Priority - A port priority can be set between 0 to 255. The lower the priority, the greater the probability the port will be chosen as the root port. • Status - Displays the status for the corresponding port. • Group Name - Displays the previously assigned name for the STP group the corresponding port belongs to. • Fast STP - Allows you to set the delay to Enabled or Disabled. Port Trunking Port trunks can be used to increase the bandwidth of a network connection or to ensure fault recovery. You can configure up to 4 trunk connections (combining 2 to 8 ports into a fat pipe) between any two DGS-3308 or other Layer 2 switches. However, before making any physical connections between devices, use the Trunk Configuration menu to specify the trunk on the devices at both ends. When using a port trunk, note that: • The ports used in a trunk must all be of the same media type (RJ-45, 100 Mbps fiber, or 1000 Mbps fiber). The ports that can be assigned to the same trunk have certain other restrictions (see below). • Ports can only be assigned to one trunk. • The ports at both ends of a connection must be configured as trunk ports. • None of the ports in a trunk can be configured as a mirror source port or a mirror target port. • All of the ports in a trunk have to be treated as a whole when moved from/to, added or deleted from a VLAN. • The Spanning Tree Protocol will treat all the ports in a trunk as a whole. 176