D-Link DGS-3308FG Product Manual - Page 194
Static Setup
 |
UPC - 790069239373
View all D-Link DGS-3308FG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 194 highlights
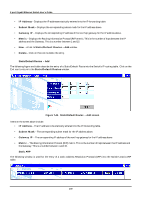
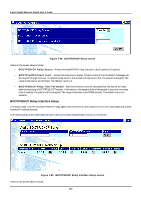
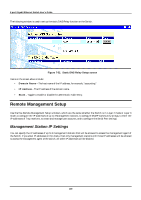
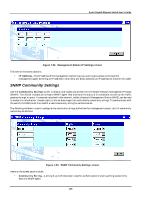
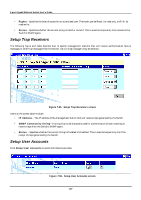
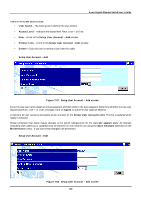
8-port Gigabit Ethernet Switch User's Guide • Interface Name - The subnet name, or IP interface name, of the network that the BOOTP server is located on. • BOOTP/DHCP Server - The IP address of the BOOTP/DHCP relay server. Multiple servers may be entered for a given subnet name (IP interface name). • Remove - Click on the icon to remove the entry from the table. DNS Relay DNS relay enables end stations to use a DNS server to resolve domain names into IP addresses, even if the server and the end station are not on the local IP interface. If the DNS server and end station are on the same IP interface, no relay is necessary. If the servers and the end stations are on different IP interfaces, a relay agent is necessary for the switch to forward the messages. The relay agent forwards these packets between IP interfaces, and therefore must know the IP addresses of the DNS servers and their respective subnet names (or IP interface names). When the switch receives packets destined for a DNS server, it forwards them to specific servers as defined in the following configuration. The Switch also forwards packets from the DNS servers to the appropriate subnets. The first task is to set some parameters for the relay agent to decide whether or not to forward a given DNS packet. Figure 7-51. DNS Relay Setup screen Items on the screen above include: • DNS Relay State - Allows the DNS relay function to be Enabled or Disabled on the Switch. • Primary Name Server - The IP address of the primary DNS server. • Secondary Name Server - The IP address of a secondary DNS server. • DNS Relay Cache Server Status - Allows the DNS cache on the Switch to be Enabled or Disabled. • DNS Relay Static Table Lookup Status - Allows the DNS Static Table Lookup function on the Switch to be Enabled or Disabled. Static Setup The second task is to tell the DNS relay agent where the servers are located in terms of IP addresses and subnet names (IP interface names). 184