D-Link DGS-3308FG Product Manual - Page 209
GVRP Status screen, Browse Router Port screen
 |
UPC - 790069239373
View all D-Link DGS-3308FG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 209 highlights
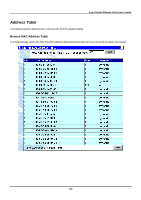
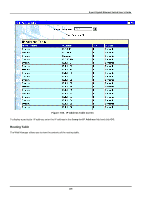
8-port Gigabit Ethernet Switch User's Guide Figure 7-68. GVRP Status screen Browse Router Port A static router port is simply a port that has a router attached to it. Generally, this router would have a connection to a WAN or to the Internet. Establishing a router port allows multicast packets coming from the router to be propagated throughout the network, as well as allowing multicast messages coming from the network to be propagated to the attached router. The purpose of a router port is to enable UDP multicast packets, and IGMP multicast group membership messages to reach multiple ports of a multicast-enabled router. Routers do not implement IGMP snooping or transmit/forward IGMP report packets. Thus, forwarding all IP UDP multicast packets to a static router port guarantees that all ports of a multicast-enabled router - attached to the Switch - can reach all multicast group members through the attached router's other ports. The Switch monitors each port for UDP multicast packets and IGMP multicast group membership reports. When these packets are detected on a port, that port is dynamically assigned as router port. Figure 7-69. Browse Router Port screen Items on the screen above include: • Jump to VID - Allows a VID to be specified to search the router port table with. • Go - Click this button to search the router port table using the VID entered above. • VID - The VLAN ID number. 199