Dell PowerEdge XL 5133-4 MXL 10/40GbE Switch IO Module FTOS Command Reference - Page 127
Leaving and Staying in Groups, IGMP Snooping
 |
View all Dell PowerEdge XL 5133-4 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 127 highlights
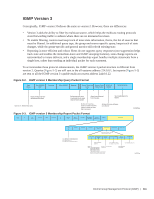
Leaving and Staying in Groups Figure 9-5 shows how multicast routers track and refresh state changes in response to group-and-specific and general queries. 1. Host 1 sends a message indicating it is leaving group 224.1.1.1 and that the included filter for 10.11.1.1 and 10.11.1.2 are no longer necessary. 2. The querier, before making any state changes, sends a group-and-source query to see if any other host is interested in these two sources; queries for state-changes are retransmitted multiple times. If any are interested, they respond with their current state information and the querier refreshes the relevant state information. 3. Separately in Figure 9-5, the querier sends a general query to 224.0.0.1. 4. Host 2 responds to the periodic general query so the querier refreshes the state information for that group. Figure 9-5. IGMP Membership Queries: Leaving and Staying in Groups Membership Queries: Leaving and Staying Querier Interface Multicast Group Filter Source Source Address Timer Mode Timer 1/1 224.1.1.1 Include 10.11.1.1 LQMT 1/1 10.11.1.2 LQMT 224.2.2.2 GMI Exclude None IGMP Group-and-Source Specific Query Type: 0x11 Group Address: 224.1.1.1 Number of Sources: 2 Source Address: 10.11.1.1, 10.11.1.2 1 Non-querier builds identical table and waits Other Querier Present Interval to assume Querier role Queries retransmitted Last Member Query Count times at Last Member 2 Query Interval Type: 0x17 Number of Group Records: 1 Record Type: 6 4 Number of Sources: 2 Multicast Address: 224.1.1.1 Source Addresses: 10.11.1.1, 10.11.1.2 IGMP Leave message Non-Querier 2/1 Type: 0x11 3 Group Address: 224.0.0.1 Number of Sources: 0 IGMP General Membership Query Type: 0x22 Number of Group Records: 1 Record Type: 2 Number of Sources: 0 Multicast Address: 224.2.2.2 IGMP Membership Report Host 1 Host 2 IGMP Snooping IGMP snooping is auto-configured on an Aggregator. Multicast packets are addressed with multicast MAC addresses, which represent a group of devices rather than one unique device. Switches forward multicast frames out of all ports in a VLAN by default, even if there are only a small number of interested hosts, resulting in a waste of bandwidth. IGMP snooping enables switches to use information in IGMP packets to generate a forwarding table that associates ports with multicast groups so that received multicast frames are forwarded only to interested receivers. Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) | 113