D-Link DNS-1250-04 User Manual for DNS-1250-04 - Page 63
Transition, Running a Background Activity, AdminTool, Background Activity, Start
 |
View all D-Link DNS-1250-04 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
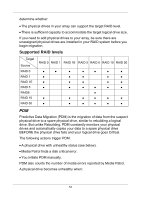
Page 63 highlights
A SMART error is reported. The bad sector remapping table fills to the specified level. You can specify the maximum levels for the reassigned and error blocks in PDM settings. When the table fills to a specified value, PDM triggers a migration of data from the suspect drive (the physical drive with the bad sectors) to a replacement drive. During data migration, you have access to your logical drives but they respond more slowly to read/write tasks because of the additional operation. The time required for data migration depends on the size of the physical drives. PDM is enabled on all disk arrays by default. You can disable PDM in the disk array settings, however that action is not recommended. Transition Transition is the process of replacing a revertible spare drive that is currently part of a disk array with an un-configured physical drive or a non-revertible spare. The revertible spare drive returns to its original status. In order to run the Transition function, the spare drive must be revertible. In addition, you must specify an un-configured physical drive of the same or larger capacity and same media type as the revertible spare drive. Synchronization Synchronization is automatically applied to logical drives when they are created. Synchronization recalculates the redundancy data to ensure that the working data on the physical drives is properly in sync. Mouse-over on the logical drive, click the View button, and look under Logical Drive Information beside the line that says Synchronized. A Yes means the logical drive was synchronized. Running a Background Activity To run a background activity: 1. Click the AdminTool tab. 2. Click the Background Activity button. 3. Click the Start button beside the activity you want to run. 55