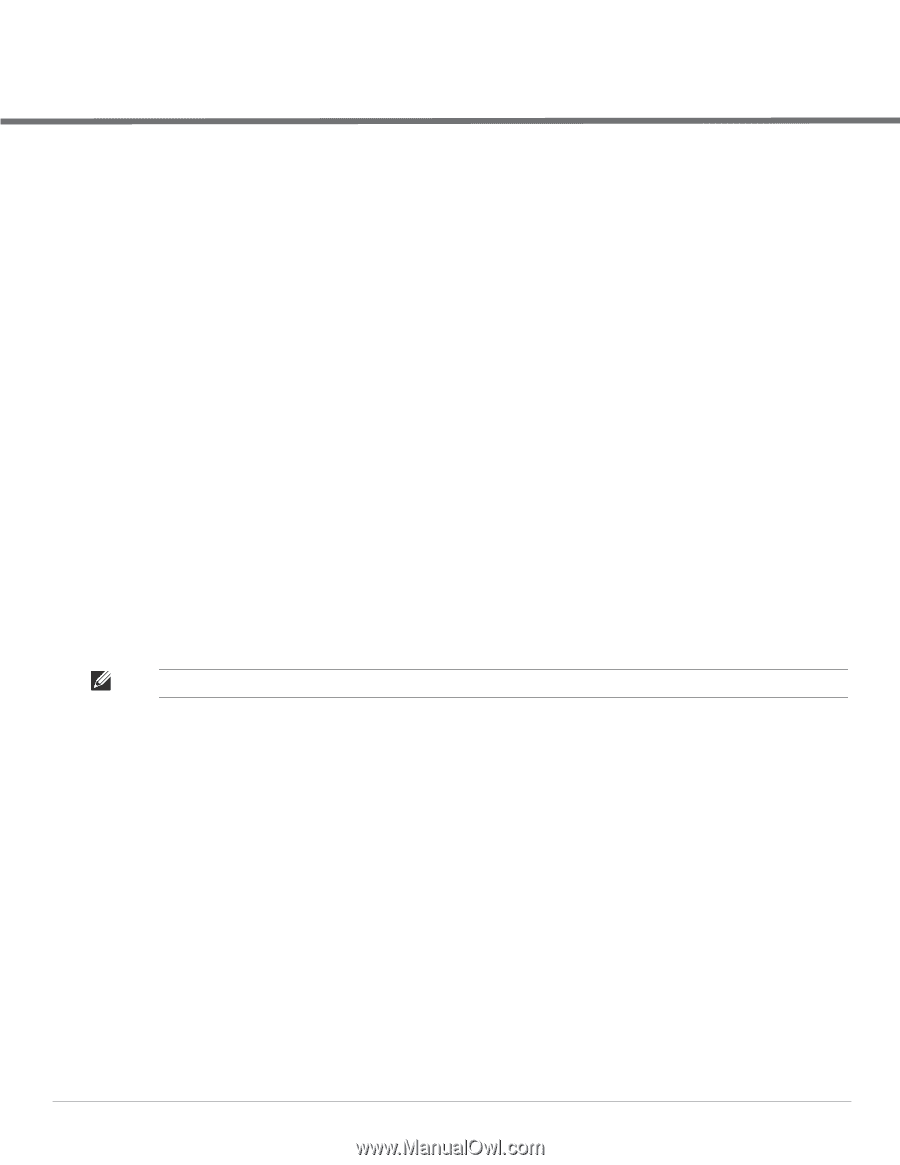Dell PowerConnect W-IAP92 Dell Instant 6.1.3.1-3.0.0.0 User Guide - Page 117
Encryption, Encryption Types Supported in Dell Instant, WEP, TKIP, AES, Encryption Recommendations
 |
View all Dell PowerConnect W-IAP92 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 117 highlights
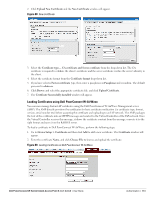
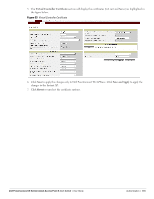
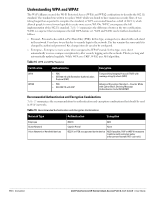
Chapter 9 Encryption Encryption Types Supported in Dell Instant Encryption is the process of converting data into an undecipherable format or code when it is transmitted on a network. Encryption prevents unauthorized use of the data. The following encryption types are supported in Dell Instant: WEP Though WEP is an authentication method, it is also an encryption algorithm where all users typically share the same key. WEP is easily broken with automated tools, and should be considered no more secure than an open network. It is recommended against deploying WEP encryption. Organizations that use WEP are strongly encouraged to move to Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption. TKIP TKIP uses the same encryption algorithm as WEP, but TKIP is much more secure and has an additional message integrity check (MIC). Recently some cracks have begun to appear in the TKIP encryption methods. It is recommended that all users migrate from TKIP to AES as soon as possible. AES The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption algorithm is now widely supported and is the recommended encryption type for all wireless networks that contain any confidential data. AES in Wi-Fi leverages 802.1X or PSKs to generate per station keys for all devices. AES provides a high level of security, similar to what is used by IP Security (IPsec) clients. It is recommended that all devices be upgraded or replaced so that they are capable of AES encryption. NOTE: WEP and TKIP are limited to WLAN connection speed of 54 Mbps. For 802.11n connection only AES encryption is supported. Encryption Recommendations Recommendations for encryption on Wi-Fi networks are as follows: WEP -Not recommended TKIP- Not recommended AES- Recommended for all deployments Dell PowerConnect W-Series Instant Access Point 6.1.3.1-3.0.0.0 | User Guide Encryption | 117