Dell PowerConnect W-IAP92 Dell Instant 6.1.3.1-3.0.0.0 User Guide - Page 45
Table 4, b. Broadcast/Multicast, Multicast optimization, Enabled, Broadcast filtering
 |
View all Dell PowerConnect W-IAP92 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 45 highlights
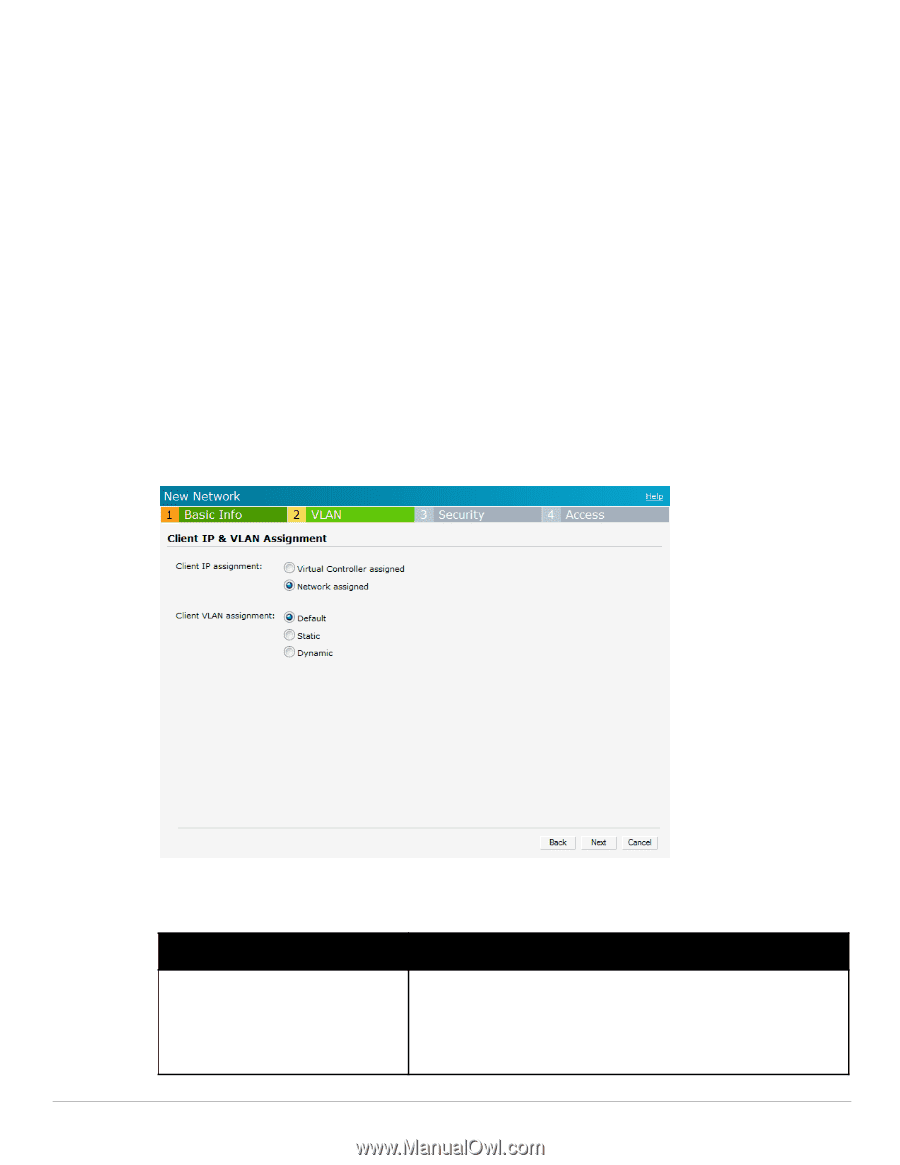
Each radio- Indicates the aggregate amount of throughput each radio (some AP models have multiple radios) is allowed to provide for all clients connected to that radio. b. Broadcast/Multicast Multicast optimization- When Enabled, the IAP will choose the optimal rate for sending broadcast and multicast frames based on the lowest of unicast rates across all associated clients. The default values are 1 mbps for 2.4GHz and 6 mbps for 5.0GHz bands. Multicast traffic can be sent at up to 24 mbps when this option is enabled. This option is disabled by default. Broadcast filtering- When set to All, the IAP will drop all broadcast and multicast frames except for DHCP and ARP. When set to ARP, in addition to the above, the IAP will convert ARP requests to unicast and send frames directly to the associated client. When Disabled, all broadcast and multicast traffic is forwarded. DTIM interval- Indicates the DTIM (delivery traffic indication message) period in beacons. You can configure this option for every WLAN SSID profile. The default value is 1, which means the client will check for buffered data on the IAP at every beacon. You may choose to configure a larger DTIM value for power saving. c. Transmit Rates- Indicates the ability to configure the basic and supported rates per SSID for Dell Instant. Select to set the minimum and maximum legacy (non-802.11n) transmit rates for each band - 2.4GHz and 5GHz. 4. Click Next to continue. Figure 32 Adding an Employee Network- VLAN Tab 5. Select the required Client IP assignment option - Virtual Controller assigned and Network assigned. Table 4 Conditions for Client IP and VLAN assignment If then You select Virtual Controller assigned The client gets the IP address from the Virtual Controller. The Virtual Controller creates a private subnet and VLAN on the IAP for the wireless clients. The Virtual Controller NATs all traffic that passes out of this interface. This setup eliminates the need for complex VLAN and IP address management for a multi site wireless network. See Chapter 7, "Virtual Controller" on page 91 for configuring the DHCP server. Dell PowerConnect W-Series Instant Access Point 6.1.3.1-3.0.0.0 | User Guide Wireless Network | 45