Lenovo ThinkPad T520 (English) User Guide - Page 76
Modem commands, Examples: ATL[Ent
 |
View all Lenovo ThinkPad T520 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 76 highlights
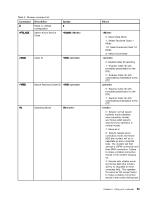
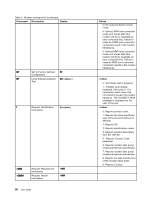
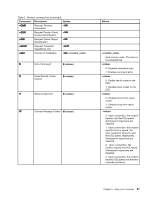
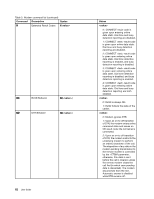
• Fast Connect Note: This function can work only if the phone line and server equipment at your ISP (Internet Service Provider) access point are compatible with it. Check with your telephone company and ISP. • Modem on Hold Note: This function can be used only in certain countries or regions, because it relies on the specifications of the Call Waiting function and Caller ID function, which each country or region sets independently. It has been tested and shown to work in the United States and Canada. In addition, the function can work only if it is compatible with the server equipment at your ISP. Industry standard fax support up to 14.4 Kbps: Fax protocols • V.21 Ch 2 (300-bps fax) • V.17 (up to 14.4-Kbps fax) • V.29 (9600-bps fax) • V.27ter (4800-bps fax) Computer telephony function support: • DTMF and pulse dialing • Detecting DTMF digits received from the phone line • Call progress monitoring • An auto-dialing feature • Telephony API (TAPI) Modem commands This section provides information on the AT modem commands, in case you need to operate your modem from terminal software. Running commands Your modem is in command mode at power-on and is ready to receive and run AT commands. It remains in command mode until it connects with a remote modem. You can send commands to the modem from an attached terminal or a PC running a communication program. The modem is designed to operate at common DTE speeds ranging from 115.2 Kbps (or 57.6 Kbps) to 300 Kbps. All commands and data must be issued to the modem at one of the valid DTE speeds. Command format All commands except A/ must begin with the prefix AT, followed by the command letter, and must end with the Enter key. Spaces are allowed in the command string to increase readability, but the modem ignores them while executing a command. All commands may be typed in either uppercase or lowercase, but not in mixed case. A command issued without a parameter is considered to have parameter "0". Examples: ATL[Ent er] This command causes your modem to lower the volume from its speaker. Refer to the following tables of AT commands and extended AT commands. 58 User Guide