TP-Link T3700G-28TQ T3700G-28TQ V1 UG - Page 186
Link State Database, OSPF Protocol Packet Type, Discontinuous Network Segment
 |
View all TP-Link T3700G-28TQ manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 186 highlights
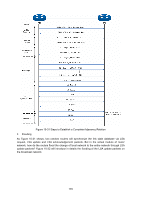
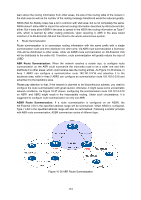
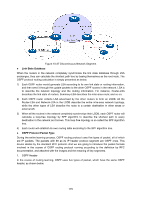
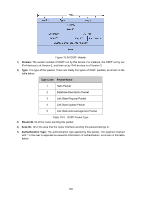
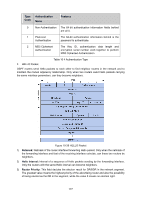
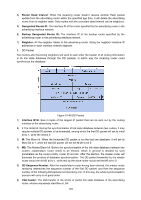
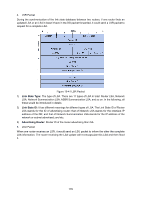
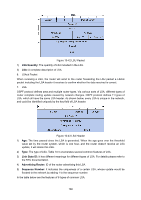
Figure 10-37 Discontinuous Network Segment Link State Database When the routers in the network completely synchronize the link state database through LSA exchanges, they can calculate the shortest path tree by basing themselves as the root node. The OSPF protocol routing calculation is simply presented as below. 1) Each OSPF router would generate LSA according to its own link state or routing information, and then send it through the update packets to the other OSPF routers in the network. LSA is to describe the network topology and the routing information. For instance, Router-LSA describes the link state of routers; Summary-LSA describes the inter-area route; and so on. 2) Each OSPF router collects LSA advertised by the other routers to form an LSDB. All the Router-LSA and Network-LSA in the LSDB describe the entire intra-area network topology, while the other types of LSA describe the route to a certain destination in other areas or external AS. 3) When all the routers in the network completely synchronize their LSDB, each OSPF router will calculate a loop-free topology by SPF algorithm to describe the shortest path to every destination in the network as it knows. This loop-free topology is so-called the SPF algorithm tree. 4) Each router will establish its own routing table according to the SPF algorithm tree. OSPF Protocol Packet Type During the entire learning process, OSPF routing protocol uses five types of packet, all of which are IP packets. The packets with 89 as its IP header protocol segment are OSPF ones. This device abides by the standard RFC protocol. And we are going to introduce the packet formats involved in the course of OSPF routing protocol running according to the definition by RFC documentation, and attached with the images and the meaning of key segments. 1. OSPF Header In the course of routing learning, OSPF uses five types of packet, which have the same OSPF header, as shown below. 175