TP-Link T3700G-28TQ T3700G-28TQ V1 UG - Page 331
TLV Type, TLV Name, Description, Usage in, LLDPDU, Any information following an End Of LLDPDU
 |
View all TP-Link T3700G-28TQ manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 331 highlights
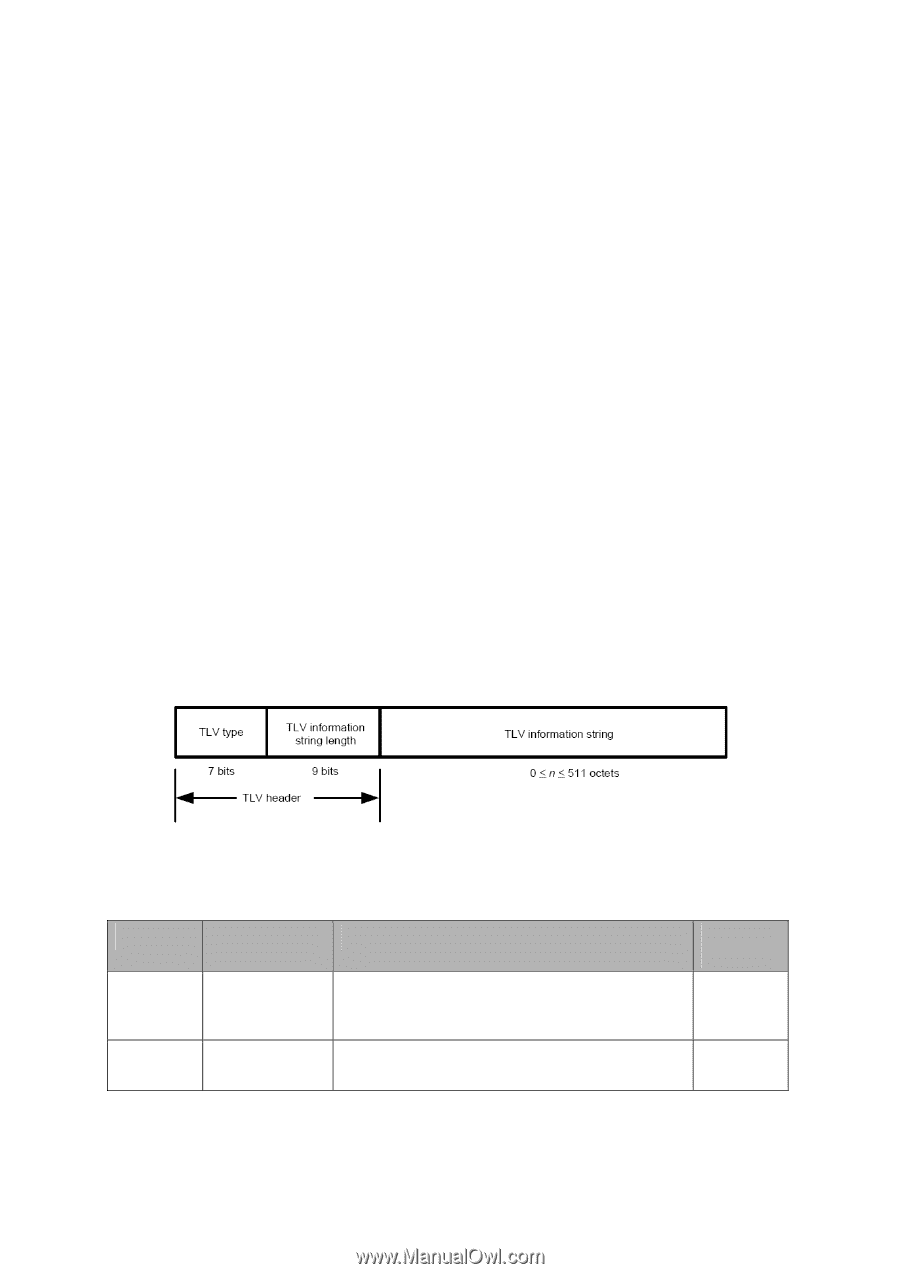
Disable: the port cannot transmit or receive LLDPDUs. 2) LLDPDU transmission mechanism If the ports are working in TxRx or Tx mode, they will advertise local information by sending LLDPDUs periodically. If there is a change in the local device, the change notification will be advertised. To prevent a series of successive LLDPDUs transmissions during a short period due to frequent changes in local device, a transmission delay timer is set by network management to ensure that there is a defined minimum time between successive LLDP frame transmissions. If the LLDP admin status of the port is changed from Disable/Rx to TxRx/Tx, the Fast Start Mechanism will be active, the transmit interval turns to be 1 second, several LLDPDUs will be sent out, and then the transmit interval comes back to the regular interval. 3) LLDPDU receipt mechanism When a port is working in TxRx or Rx mode, the device will check the validity of the received LLDPDUs and the attached TLVs, save this neighbor information to the local device and then set the aging time of this information according to the TTL value of TTL (Time To Live) TLV. Once the TTL is 0, this neighbor information will be aged out immediately. The aging time of the local information in the neighbor device is determined by TTL. Hold Multiplier is a multiplier on the Transmit Interval that determines the actual TTL value used in an LLDPDU. TTL = Hold Multiplier * Transmit Interval. TLV TLV refers to Type/Length/Value and is contained in a LLDPDU. Type identifies what kind of information is being sent, Length indicates the length of information string in octets and Value is the actual information to be sent. The basic TLV Format is shown as follows: Each TLV is identified by a unique TLV type value that indicates the particular kind of information contained in the TLV. The following table shows the details about the currently defined TLVs. TLV Type 0 1 TLV Name Description Usage in LLDPDU End of LLDPDU Mark the end of the TLV sequence in LLDPDUs. Mandatory Any information following an End Of LLDPDU TLV shall be ignored. Chassis ID Identifies the Chassis address of the connected Mandatory device. 320