TP-Link T3700G-28TQ T3700G-28TQ V1 UG - Page 235
Packet Statistics, 11.3 PIM DM
 |
View all TP-Link T3700G-28TQ manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 235 highlights
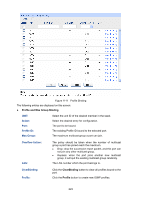
11.2.6 Packet Statistics On this page you can view multicast packet statistics over each interface of the switch, which facilitates you monitor the IGMP packets in the network. Choose the menu Multicast Routing→IGMP→Packet Statistics to load the following page. Figure 11-10 Packet Statistics The following entries are displayed on this screen: Auto Refresh Auto Refresh: Refresh Period: IGMP Statistics Select Enable/Disable auto refresh feature. Enter the time from 3 to 300 in seconds to specify the auto refresh period. Interface: Query Packet: Report Packet(V1): Report Packet(V2): Report Packet(V3): Leave Packet: Error Packet: Displays the interface. Displays the number of query packets the interface received. Displays the number of IGMPv1 report packets the interface received. Displays the number of IGMPv2 report packets the interface received. Displays the number of IGMPv3 report packets the interface received. Displays the number of leave packets the interface received. Displays the number of error packets the interface received. 11.3 PIM DM PIM (defined in RFC 3973) is a popular multicast routing protocol within the AS. Instead of relying on one specific unicast routing protocol, PIM uses the static routing or unicast routing table generated by any unicast routing protocol (including RIP, OSPF, IS-IS, BGP etc) to perform routing for IP multicast data. Unlike some other multicast routing protocols, PIM doesn't update routing information between routers or maintain an independent route forwarding table. PIM uses the RPF (Reverse Path Forwarding) check mechanism to forward the multicast data. There are two types of multicast routing and forwarding tables in the multicast implementation: All the multicast route information will be summarized as a general multicast routing-table; 224