TP-Link T3700G-28TQ T3700G-28TQ V1 UG - Page 222
Global Config, 11.1.2 Mroute Table
 |
View all TP-Link T3700G-28TQ manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 222 highlights
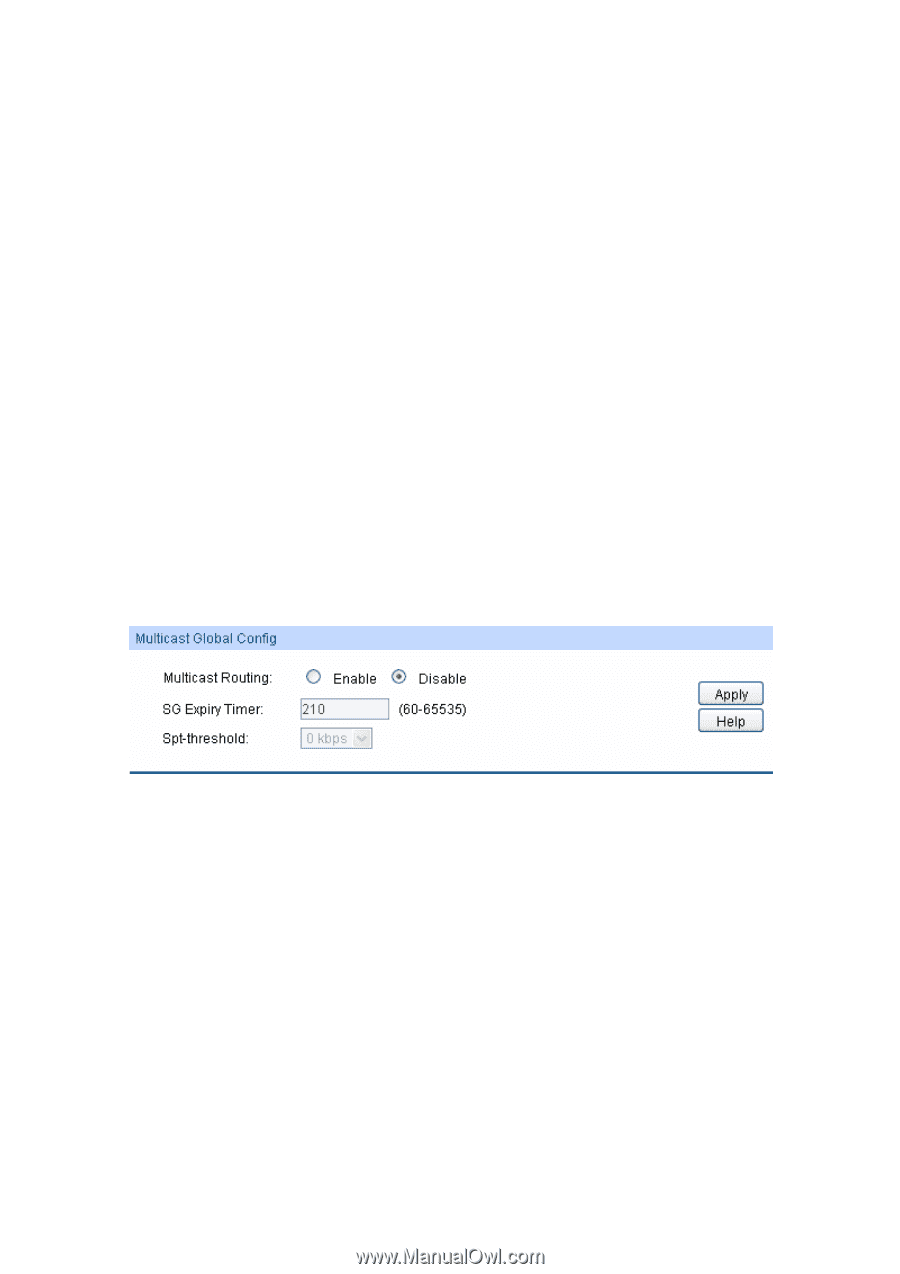
The multicast model divides into two types depending on whether there is an exact multicast source: ASM (Any-Source Multicast) and SSM (Source-Specific Multicast). ASM (Any-Source Multicast): In the ASM model, any sender can be a multicast source sending multicast information to a multicast group address, and receivers can join a multicast group identified by the group address and obtain multicast information addressed to that multicast group. In this model, receivers are not aware of the location of the multicast source in advance. However, they can join or leave the multicast group at any time. At any specified moment, the number of multicast source in the ASM should be no more than one, otherwise network congestion and malfunction of the multicast members may occur. SSM (Source-Specific Multicast): In the SSM model, the receivers know the exact location of the multicast source. The SSM allows host to specify the multicast sources and it uses the multicast group address range different from that of the ASM. The SSM marks a multicast session with both multicast address and multicast source address, and it builds up dedicated multicast forwarding path for the receiver and its specified multicast source. 11.1 Global Config The Global Config can be implemented on the Global Config and Mroute Table pages. 11.1.1 Global Config You must enable IP multicast routing. Then the software can forward multicast packets, and the switch can populate its multicast routing table. Choose the menu Multicast Routing→Global Config→Global Config to load the following page. Figure 11-1 multicast Global Config The following entries are displayed on this screen: Multicast Global Config Multicast Routing: SG Expiry Timer: Spt-threshold: Select Enable/Disable Multicast Routing function globally on the switch. The default is "disable". SG Expiry Timer is used to adjust (S, G) expiry timer interval for (S, G) multicast routers. The range is from 60 to 65535 seconds. Select rate which the last-hop router will switch to a source-specific shortest path tree. Specify infinity if you want all sources for the specified group to use the shared tree, never switching to the source tree. The default is 0 kbps. 11.1.2 Mroute Table On this page you can get the desired mroute information through different search options. Choose the menu Multicast Routing→Global Config→Mroute Table to load the following page. 211