TP-Link T3700G-28TQ T3700G-28TQ V1 UG - Page 192
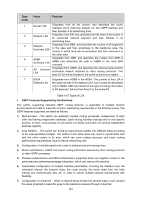
Features, OSPF Features Supported by the Switches, Table 10-5 Types of LSA
 |
View all TP-Link T3700G-28TQ manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 192 highlights
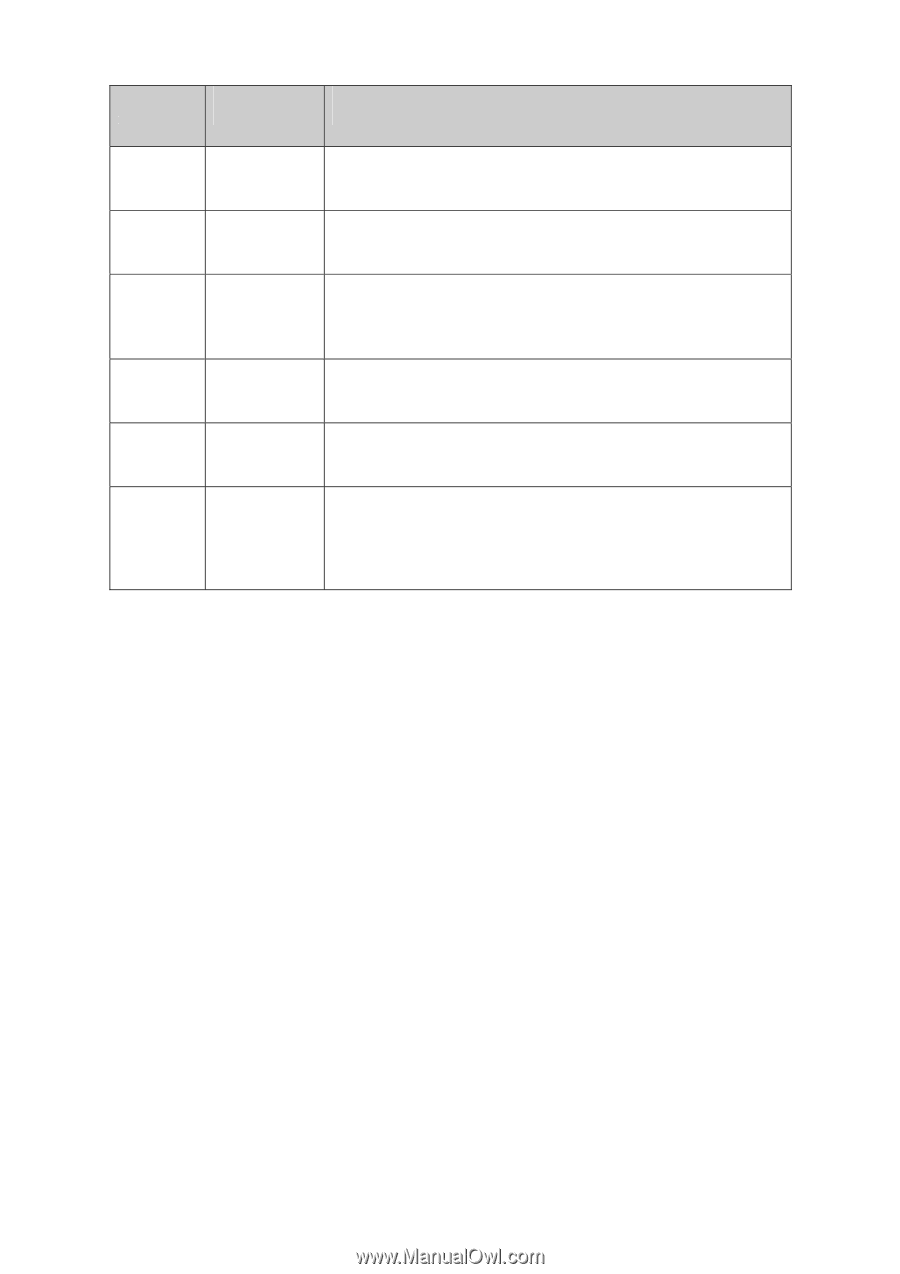
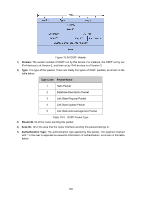
Type Code 1 2 3 4 5 7 Name Features Router LSA Network LSA Network Summary LSA ASBR Summary LSA AS External LSA Originates from all the routers, and describes the router interface which itself has already run the OSPF features and then spreads in its advertising area. Originates from DR, and describes the link state of all routers in its connected network segment and then diffuses in its advertising area. Originates from ABR, and describes the routers of all segments in the area and then advertises to the backbone area, the routers in which area will re-summarize and then announce to the other area. Originates from ABR, and describes the routers from ABR to ASBR and advertises the path to ASBR to the area ABR connects. Originates from ASBR, and describes the external route and the accessible network obtained by other routing protocols. This type of LSA will be flooded to the entire autonomous system. NSSA External LSA Originates from ASBR in the NSSA. The content of this LSA is the same as that of AS external LSA, but it would be advertised only to NSSA. ABR can transform this type of routing information to AS external LSA and then flood it to the entire AS. Table 10-5 Types of LSA OSPF Features Supported by the Switches This switch, supporting standard OSPF routing features, is applicable to multiple network environments and able to meet the common networking requirements in the Ethernet scene. The OSPF features supported are listed as follows. 1) Multi-process - The switch can establish multiple routing processes, independent of each other and having independent database. Each routing interface belongs only to one specific process. In short, multi-process on one switch is to divide one switch into several independent switches logically. 2) Area Partition - The switch can divide an autonomous system into different areas according to the user-specified principle. The routers in the same area only need to synchronize LSA with the other routers in its area, which can save routing resources and lower routing performance requirements, thus to reduce networking cost. 3) Configuration of multiple equal-cost routes to balance load and backup lines. 4) Route redistribution -OSPF can import routing information learned by other routing protocols or other OSPF processes. 5) Plaintext authentication and MD5 authentication supported when two neighbor routers in the same area are performing message interaction, which can improve the security. 6) Customized configuration of multiple interface parameters, including the interface cost, the retransmit interval, the transmit delay, the router priority, the router dead time, the hello interval and authentication key, etc. in order to satisfy multiple network requirements with flexibility. 7) Configuration of virtual link - When a network being divided into several areas, it can connect the areas physically located far away to the backbone network through virtual link. 181