TP-Link T3700G-28TQ T3700G-28TQ V1 UG - Page 247
PIM SM Interface, Asserting, BSR Administrative Domain, Multicast Routing, PIM SM
 |
View all TP-Link T3700G-28TQ manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 247 highlights
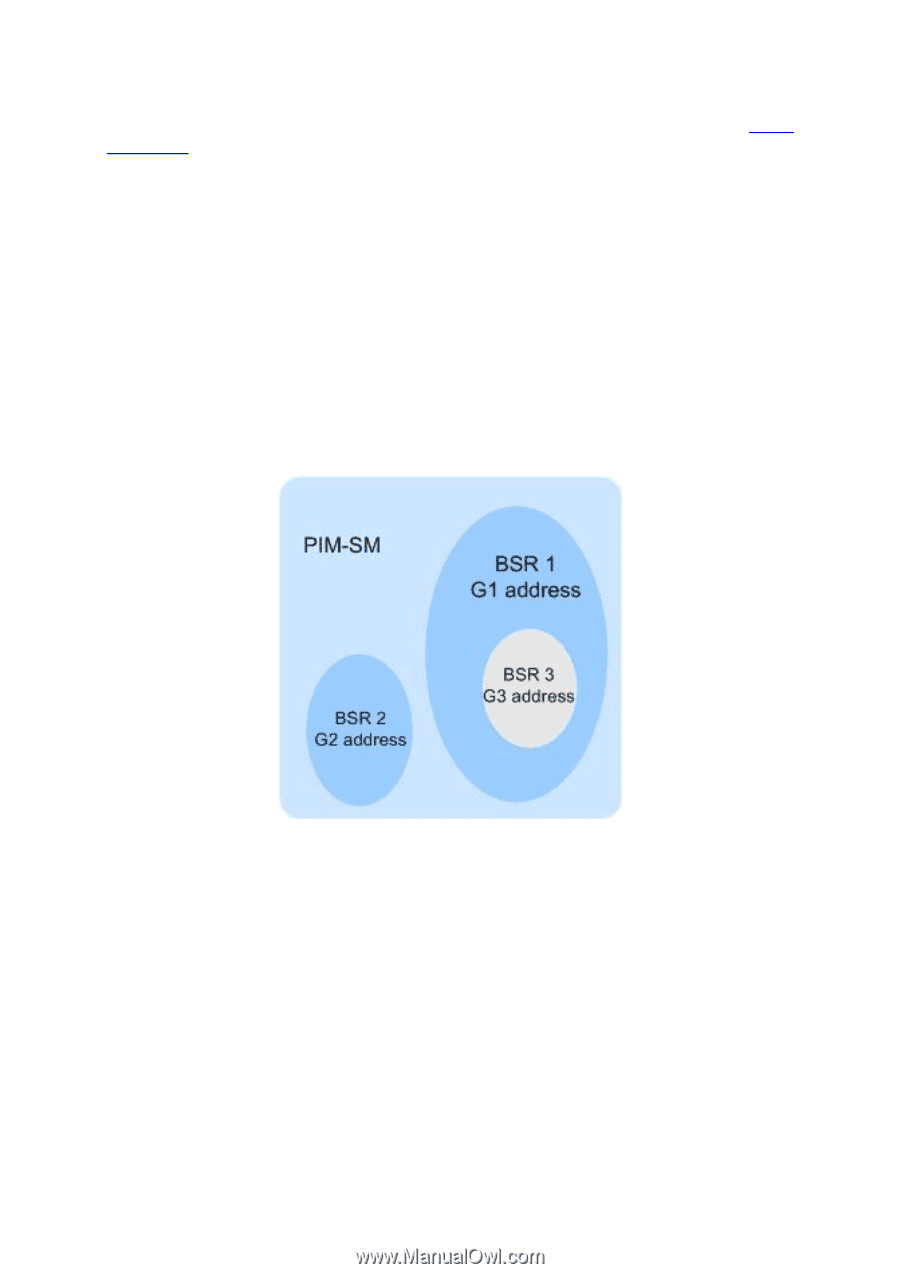
Asserting The assert mechanism of PIM SM and PIM DM is the same. For more details, refer to Assert Mechanism. BSR Administrative Domain BSR is the administrative core in the PIM SM domain. The BSR is exclusive in one PIM SM domain and it advertises the RP-Set information in the whole PIM SM domain. All the multicast group information is forwarded inside the BSR's administrative network scope. When the PIM SM domain is relatively large, you can consider dividing the PIM SM domain into multiple BSR administrative domains, thus sharing the administrative pressure of single BSR and providing specialized services for specific multicast groups. In geographical space, the BSR administrative domains are separated with each other and one router cannot belong to more than one BSR domain. In other words, the routers contained by the BSR domains are different from each other. In multicast address, each BSR administrative domain provides services for specific multicast groups. These multicast group addresses usually have no intersection with each other, but they may also have crossings and overlaps, as shown in Figure 11-19. Figure 11-19 BSR Domain Divided by Multicast Address Features of BSR administrative domain: Divide the BSR administrative domains by setting BSR border Each BSR administrative domain has its own border, C-RP and BSR devices. These devices are only valid in their belonged domains, which means that the BSR mechanism and RP election are separated between their administrative domains. BSR messages cannot pass through the BSR border The multicast messages (such as C-RP Hello Message and BSR BootStrap Message) of each BSR administrative domain can't pass through the domain border. 11.4.1 PIM SM Interface Choose the menu Multicast Routing→PIM SM→PIM SM Interface to load the following page. 236