TP-Link T3700G-28TQ T3700G-28TQ V1 UG - Page 209
VRRP, Process, Area ID, Advertising Router, LSA Type, Link State ID, Sequence, Checksum, Options
 |
View all TP-Link T3700G-28TQ manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 209 highlights
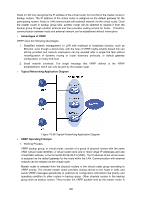
Figure10-55 Link State Database The following entries are displayed on this screen: Link State Database Process: Area ID: Advertising Router: Select one OSPF Process to display its link state database. Displays the ID of the area to which the LSA belongs. Displays the ID of the router that advertising the LSA. LSA Type: Link State ID: Age: Sequence: Checksum: Options: The format and function of the link state advertisement. One of the following: Router, Network, Network-Summary, ASBR-Summary, External (Type 5), NSSA-External (Type 7). The Link State ID identifies the piece of the routing domain that is being described by the advertisement. The value of the LS ID depends on the advertisement's LS type. The time since the link state advertisement was first originated, in seconds. The sequence number field is an unsigned 32-bit integer. It is used to detect old and duplicate link state advertisements. The larger the sequence number, the more recent the advertisement. The checksum is used to detect data corruption of an advertisement. This corruption can occur while an advertisement is being flooded, or while it is being held in a router's memory. This field is the checksum of the complete contents of the advertisement, except the LS age field. The Options field in the link state advertisement header indicates which optional capabilities are associated with the advertisement. 10.10 VRRP VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol) is a fault-tolerant protocol. Generally, all hosts in a LAN (Local Area Network) would set a default route. Packets which are sent by the host and whose destination address does not belong to the local network segment will be sent to the gateway via the default route. Therefore, communication between the host and external network can be established. Once the gateway fails, all hosts of this network segment whose default next hop is the gateway will stop communicating with external network. VRRP is developed to solve the problem mentioned above and designed for LAN with multicast or broadcast function, such as Ethernet. Virtual router acts as a backup group which consists of one master router and several backup routers. The virtual router (also a backup group) has its own IP address. This IP address can be the same as the interface address of any router in the backup group. In this case, the virtual router is also called IP address owner. All physical routers in the backup group have their own IP addresses. 198