TP-Link T3700G-28TQ T3700G-28TQ V1 UG - Page 236
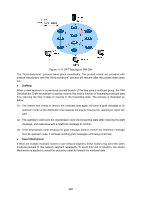
RPF Mechanism, RPF Mechanism Application
 |
View all TP-Link T3700G-28TQ manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 236 highlights
The multicast forwarding-table is used to control the forwarding of the multicast packets directly. The multicast routing table consists of a group of (S, G) entries, and (S, G) route represents routing information from source S to group G. If the router supports multiple multicast routing protocols, its multicast routing table will contain multicast routes generated from multiple protocols. The router will chose the optimal multicast route according to multicast routing and forwarding strategy, and send it to the multicast forwarding table. The multicast routing protocol uses the RPF mechanism to establish the multicast routing entries, thus to guarantee the multicast data being transferred in the correct path. RPF Mechanism PIM uses the unicast routing table to perform the RPF check. RPF mechanism ensures the multicast packets being forwarded correctly according to the multicast routing configuration, and avoids loops causing by various reasons. 1. RPF Check The RPF check relies on unicast route or static multicast route. The unicast routing table aggregates the shortest paths to each destination network segments, and the static multicast routing table lists specified static RPF routing entries configured by the user manually. Instead of maintaining certain unicast routing independently, the multicast routing protocol relies on the current unicast routing information or static multicast routing in the network to establish multicast routing entries. When performing the RPF check, the router will look up the unicast routing table and the static multicast routing table at the same time. The process is as below: (1) Chose an optimal route from the unicast routing table and the static routing table respectively: The router looks up the unicast routing table with the IP address of the packet source as the destination address, and selects an optimal unicast route automatically. The output interface of the corresponding entry is the RPF interface, and the next hop is the RPF neighbor. The router will consider the traveling path of the multicast data sent from the RPF neighbor and received on the RPF interface as the shortest path from the multicast source S to the local network. The router looks up the static multicast routing table with the IP address of the packet source specified as the source address, and selects an optimal static multicast route automatically. The corresponding entry explicitly specifies the RPF interface and RPF neighbor. (2) Select one from the two optimal routes as the RPF route: According to the longest mask matching principle, the longest mask matching route between them will be selected; if the two routes have the same mask, the route with higher priority will be selected; if the two routes also have the same priority, then the static multicast route is prior to the unicast route. 2. RPF Mechanism Application When the router receives multicast packets sent from multicast source S to multicast group G, it will look up the multicast forwarding table at first: 225