TP-Link T3700G-28TQ T3700G-28TQ V1 UG - Page 211
Authentication Methods, Master Election
 |
View all TP-Link T3700G-28TQ manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 211 highlights
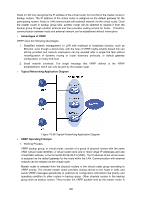
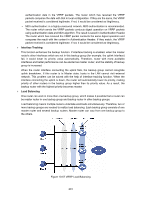
new master router will be elected among them to take the role of the master router if master router fails. 2. Master Election Initially-created routers work in Backup state and learn other members' priorities in the virtual router via VRRP packets. The one with the highest priority is elected as master router. If the priority values are the same, the router with the highest interface IP address is selected as the master. In preemptible mode, when backup router receives VRRP packet, it will compare its priority with that of the advertisement packet. If of higher priority, the backup router will become the master router; otherwise, it will maintain Backup state. In non-preemptible mode, physical routers in the backup group will maintain Master or Backup state as long as the master router functions normally. Even if backup router is given higher priority, it cannot become a master router in non-preempt mode. The VRRP priority ranges from 0 to 255 (the bigger the number is, the higher the priority is). Configurable range is 1-254. The priority value 0 is reserved for the current master when it gives up its role as master router. For example, when master router receives shutdown message, it would send VRRP packet with priority 0 to the backup group which the interface belongs to. The priority of the IP address owner must be 255. Therefore, if there exists an IP address owner in the backup group and it works normally, it must be the master router. 3. State Transition VRRP defines three state modes: Initialize, Master and Backup. Only in Master state can master router provide service for forwarding request via virtual IP address and forward VRRP packet. When the system just starts, it comes to Initialize state. If the virtual router is not given a virtual IP address, the system would maintain Initialize state. If the virtual IP address is configured properly, when the system receives startup message from interface, it would transition to the Backup state (in which case its priority is not 255) or Master state (in which case its priority is 255). Routers in master or backup state can change to Initialize state only when they receive shutdown message from interface. In Initialize state, router cannot deal with VRRP packet. If the master router functions properly, it will periodically send VRRP packets informing backup routers in the backup group that it functions properly. VRRP timer can be manually configured to customize the intervals that master router sends VRRP packet. If the backup router waits for a period longer than three times the advertisement timer and fails to receive VRRP packets from the master router, they will assume that the master router is dead and initiate an election process by transitioning to the Master state and forwarding VRRP packets. To avoid frequent Master-Backup state transition among routers in the backup group and provide enough time for backup routers to collect necessary information, backup router would not preempt to be master as soon as it receives packets with lower priority value. It would wait for a certain time, which is called preempt-mode delay time, and then send packets to take place of the former master. Users can customize the preempt-mode delay time. 4. Authentication Methods VRRP provides three authentication methods: No authentication: the eligibility of VRRP packets is not verified and no security insurance is provided. In a safe network, no authentication can be set as authentication method. Simple text password: in a network where security is possible to be threatened, simple text password is recommended. The router which forwards the VRRP packets fills the 200