TP-Link T3700G-28TQ T3700G-28TQ V1 UG - Page 246
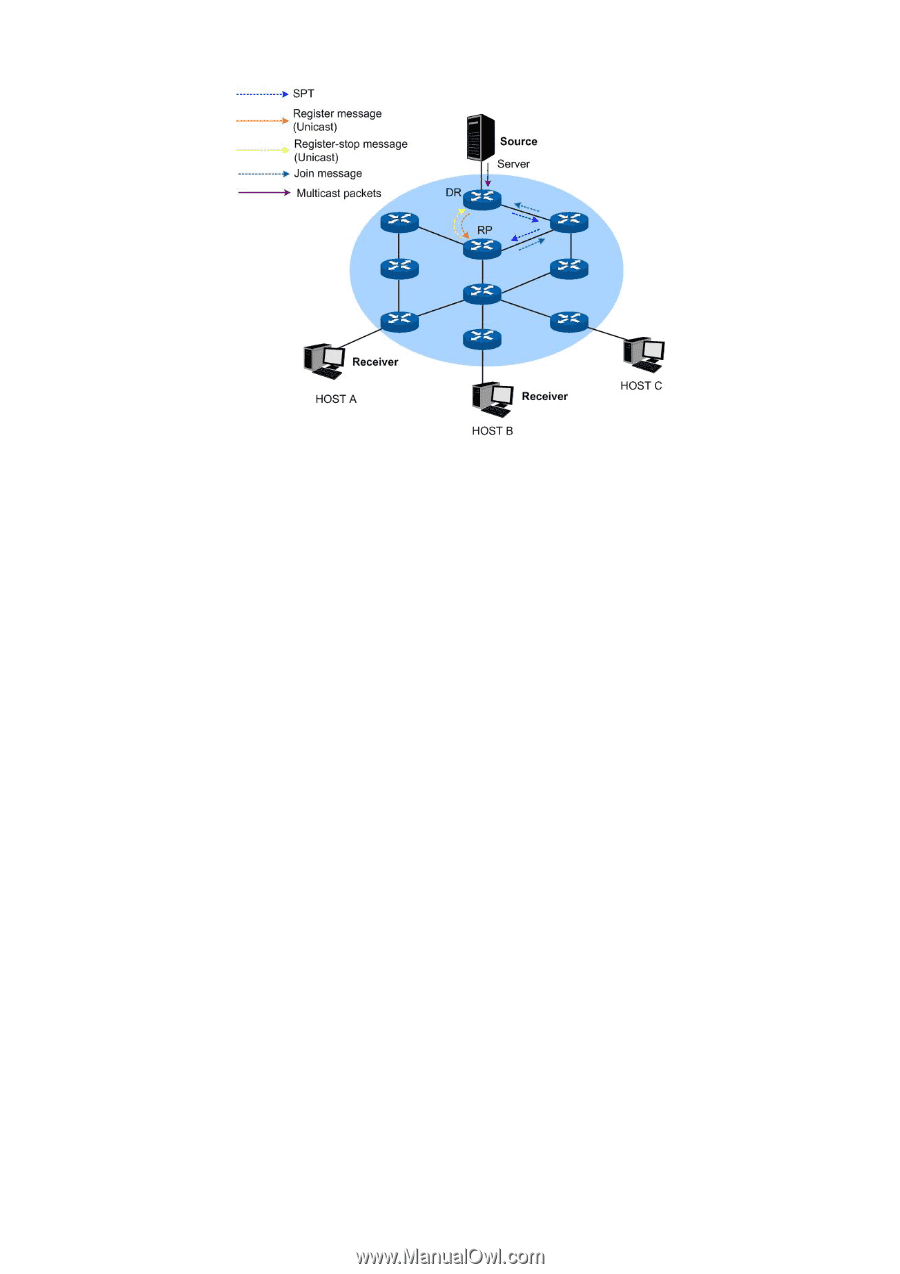
Switching from RPT to SPT, Multicast Source Register Topology in PIM SM
 |
View all TP-Link T3700G-28TQ manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 246 highlights
Figure 11-18 Multicast Source Register Topology in PIM SM (1) When the multicast source S's directly connected DR receives a multicast packet sent from the multicast source to the multicast group G, the DR will encapsulate this packet into a register packet and send it to the corresponding RP in unicast way; (2) After the RP receives the register packet, it will de-capsulate this packet and send the packaged multicast data to the receivers along the RPT, and meanwhile it will send join message to the multicast source hop-by-hop. The join message travels router-by-router toward the source from the RP, constructing a branch of the SPT as it goes. These routers generate (S, G) entries in their forwarding tables. The SPT works with multicast source as the root, and RP as the branch. (3) The multicast data sent from the multicast source travels along the constructed SPT to RP, and is forwarded by the RP to the receivers along the RPT. When RP receives the multicast data from the RPT, it will send Register-Stop Message to the DR directly connected to the multicast source to finish the multicast source register process. Switching from RPT to SPT Once receiver-side DR receives the multicast data from RP to multicast group G, the switching process from RPT to SPT will be triggered: (1) The receiver-side DR sends (S, G) join message to the multicast source S hop-by-hop, and the join message finally arrives at the source-side DR. All routers the join message passes will generate the (S, G) entry in their forwarding tables, thus building up a branch of SPT; (2) The receiver-side DR sends prune message toward the RP hop-by-hop. The RP will forward the received prune message toward the multicast source. The switching process from RPT to SPT is then accomplished. After the switching from RPT to SPT, the multicast data will be sent from multicast source to the receivers directly. Through this switching process from RPT to SPT, PIM SM constructs the SPT in a more economical way than PIM DM does. 235