Cisco 7965G Administration Guide - Page 169
Summary, Explanation, Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency
 |
UPC - 882658140464
View all Cisco 7965G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 169 highlights
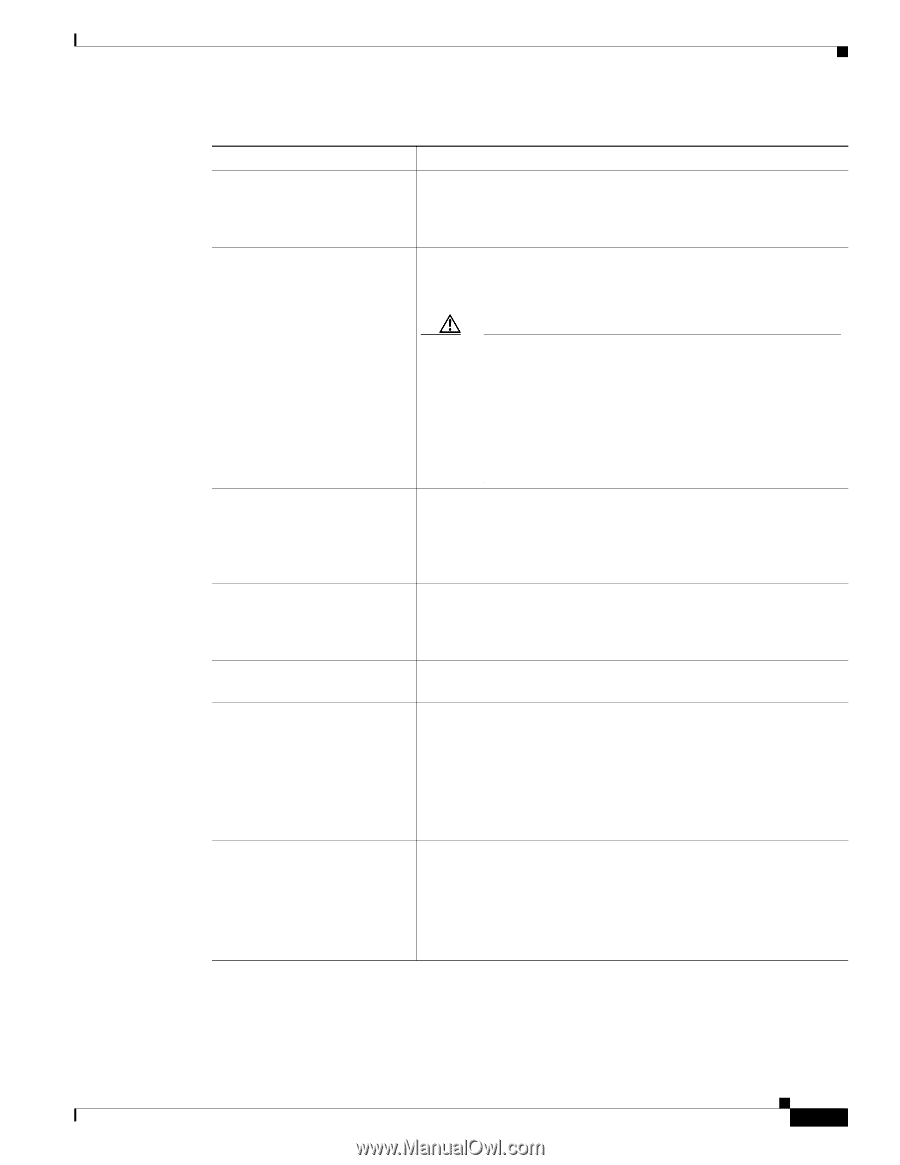
Chapter 9 Troubleshooting and Maintenance General Troubleshooting Tips Table 9-2 Cisco Unified IP Phone Troubleshooting (continued) Summary Explanation Prolonged broadcast storms A prolonged Layer 2 broadcast storm (lasting several minutes) on the cause IP phones to reset, or be voice VLAN may cause IP phones to reset, lose an active call, or be unable to make or answer a call unable to initiate or answer a call. Phones may not come up until a broadcast storm ends. Moving a network connection If you are powering your phone through the network connection, you from the phone to a workstation must be careful if you decide to unplug the phone's network connection and plug the cable into a desktop computer. Caution The computer's network card cannot receive power through the network connection; if power comes through the connection, the network card can be destroyed. To protect a network card, wait 10 seconds or longer after unplugging the cable from the phone before plugging it into a computer. This delay gives the switch enough time to recognize that there is no longer a phone on the line and to stop providing power to the cable. Changing the telephone configuration By default, the network configuration options are locked to prevent users from making changes that could impact their network connectivity. You must unlock the network configuration options before you can configure them. See the "Unlocking and Locking Options" section on page 4-3 for details. LCD display issues If the display appears to have rolling lines or a wavy pattern, it might be interacting with certain types of older fluorescent lights in the building. Moving the phone away from the lights, or replacing the lights, should resolve the problem. Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency (DTMF) delay When you are on a call that requires keypad input, if you press the keys too quickly, some of them might not be recognized. Codec mismatch between the phone and another device The RxType and the TxType statistics show the codec that is being used for a conversation between this Cisco Unified IP phone and the other device. The values of these statistics should match. If they do not, verify that the other device can handle the codec conversation, or a transcoder is in place to handle the service. See the "Call Statistics Screen" section on page 7-11 for information about displaying these statistics. Sound sample mismatch between the phone and another device The RxSize and the TxSize statistics show the size of the voice packets that are being used in a conversation between this Cisco Unified IP phone and the other device. The values of these statistics should match. See the "Call Statistics Screen" section on page 7-11 for information about displaying these statistics. OL-14641-01 Cisco Unified IP Phone 7965G and 7945G Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager 6.1 9-11