Cisco 7965G Administration Guide - Page 31
Security Restrictions, Overview of Configuring and Installing Cisco Unified IP Phones - factory reset
 |
UPC - 882658140464
View all Cisco 7965G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 31 highlights
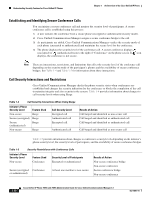
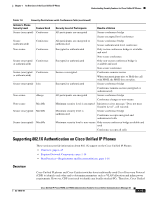
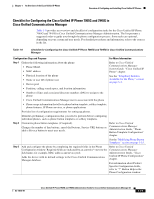
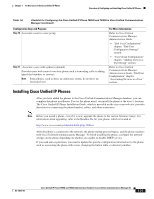
Chapter 1 An Overview of the Cisco Unified IP Phone Overview of Configuring and Installing Cisco Unified IP Phones - Disabled-If the switch does not support multiple 802.1X-compliant devices on the same port, you should disable the PC Port when 802.1X authentication is enabled. See the "Security Configuration Menu" section on page 4-25 for more information. If you do not disable this port and subsequently attempt to attach a PC to it, the switch will deny network access to the phone and the PC. • Configure Voice VLAN-Because the 802.1X standard does not account for VLANs, you should configure this setting based on the switch support. - Enabled-If you are using a switch that supports multi-domain authentication, you can continue to use the voice VLAN. - Disabled-If the switch does not support multi-domain authentication, disable the Voice VLAN and consider assigning the port to the native VLAN. See the "Security Configuration Menu" section on page 4-25 for more information. • Enter MD5 Shared Secret-If you disable 802.1X authentication or perform a factory reset on the phone, the previously configured MD5 shared secret is deleted. See the "802.1X Authentication and Status" section on page 4-34 for more information. Security Restrictions A user cannot barge into an encrypted call if the phone that is used to barge is not configured for encryption. When barge fails in this case, a reorder tone (fast busy tone) plays on the phone on which the user initiated the barge. If the initiator phone is configured for encryption, the barge initiator can barge into an authenticated or nonsecure call from the encrypted phone. After the barge occurs, Cisco Unified Communications Manager classifies the call as nonsecure. If the initiator phone is configured for encryption, the barge initiator can barge into an encrypted call, and the phone indicates that the call is encrypted. A user can barge into an authenticated call, even if the phone that is used to barge is nonsecure. The authentication icon continues to appear on the authenticated devices in the call, even if the initiator phone does not support security. Overview of Configuring and Installing Cisco Unified IP Phones When deploying a new IP telephony system, system administrators and network administrators must complete several initial configuration tasks to prepare the network for IP telephony service. For information and a checklist for setting up and configuring a complete Cisco IP telephony network, refer to the "System Configuration Overview" chapter in Cisco Unified Communications Manager System Guide. After you have set up the IP telephony system and configured system-wide features in Cisco Unified Communications Manager, you can add IP phones to the system. The following topics provide an overview of procedures for adding Cisco Unified IP Phones to your network: • Configuring Cisco Unified IP Phones in Cisco Unified Communications Manager, page 1-18 • Installing Cisco Unified IP Phones, page 1-21 OL-14641-01 Cisco Unified IP Phone 7965G and 7945G Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager 6.1 1-17