HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Fundamentals Configuration - Page 11
Entering a command, Editing a command line, Entering a STRING type value for an argument
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 11 highlights
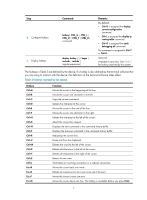
ftp ftp-server ftp-user Entering a command When you enter a command, you can use some keys or hotkeys to edit the command line, or use abbreviated keywords or keyword aliases. Editing a command line You can use the keys listed in Table 2 or the hotkeys listed in Table 3 to edit a command line. Table 2 Keys for editing a command line Key Common keys Backspace Left arrow key or Ctrl+B Right arrow key or Ctrl+F Tab Function If the edit buffer is not full, pressing a common key inserts the character at the position of the cursor and moves the cursor to the right. Deletes the character to the left of the cursor and moves the cursor back one character. Moves the cursor one character to the left. Moves the cursor one character to the right. If you press Tab after entering part of a keyword, the system automatically completes the keyword: • If a unique match is found, the system substitutes the complete keyword for the incomplete one and displays what you entered in the next line. • If there is more than one match, you can press Tab repeatedly to choose the keyword you want to enter. • If there is no match, the system does not modify what you entered but displays it again in the next line. Entering a STRING type value for an argument Generally, a STRING type argument value can contain any printable character (in the ASCII code range of 32 to 126) other than the question mark (?), quotation mark ("), backward slash (\), and space. However, a specific STRING type argument might have more strict requirements. For example, the domain name is of the STRING type. Invalid characters for it include the vertical bar (|), slash (/), colon (:), asterisk (*), less-than sign (),and at sign (@), as well as the question mark (?), quotation mark ("), backward slash (\), and space. For more information about the specific requirements for a STRING type argument, see the relevant command reference. system-view [Sysname] domain ? STRING Domain name Abbreviating commands You can enter a command line quickly by entering incomplete keywords that can uniquely identify the complete command. In user view, for example, commands starting with an s include startup 5